Where Can Earthquakes Occur
Earthquakes are natural phenomena that can strike anywhere on our planet, often without warning. These powerful events occur when there is a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust, leading to the ground shaking violently. While some regions are more prone to earthquakes than others, it is essential to understand the factors that contribute to their occurrence. In this blog post, we will explore the various places where earthquakes can happen and shed light on the underlying causes.
Understanding the Earth's Tectonic Plates

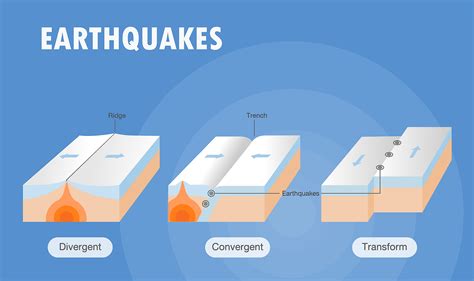
The Earth's surface is composed of several large and small tectonic plates that float on the semi-fluid mantle beneath. These plates are in constant motion, albeit at a very slow pace. The movement of these plates is a crucial factor in the occurrence of earthquakes. When two plates interact, they can either collide, slide past each other, or move away from each other, resulting in different types of seismic activity.
Collision Zones

When two tectonic plates collide, one plate may be forced beneath the other in a process called subduction. This often happens at the boundaries of oceanic and continental plates. The subduction zone is a highly active area, where earthquakes can occur frequently. Some of the most powerful earthquakes in history have taken place in these collision zones, such as the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami, which had a magnitude of 9.1.
Transform Boundaries

Transform boundaries occur when two plates slide past each other horizontally. The San Andreas Fault in California is a well-known example of a transform boundary. As the plates grind against each other, stress builds up, and when it exceeds the strength of the rocks, an earthquake occurs. These types of earthquakes can cause significant damage, as seen in the 1906 San Francisco earthquake.
Divergent Boundaries

Divergent boundaries are areas where two tectonic plates move away from each other. This often happens in the middle of oceans, where new crust is formed. As the plates separate, molten rock rises to fill the gap, leading to the formation of volcanic islands. While earthquakes at divergent boundaries are generally less intense than those at collision zones, they can still be quite powerful, as seen in the 1964 Alaska earthquake, which had a magnitude of 9.2.
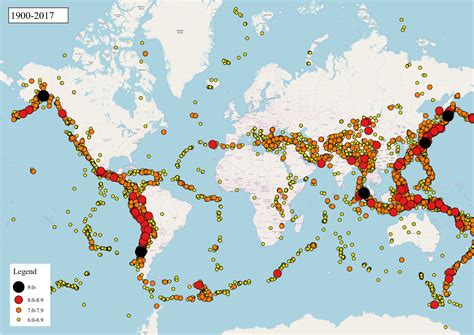
Earthquakes Around the World

Earthquakes can occur in various regions across the globe, but some areas are more seismically active than others. Here are a few regions where earthquakes are more prevalent:
The Pacific Ring of Fire

The Pacific Ring of Fire, also known as the Circum-Pacific Belt, is a region that surrounds the Pacific Ocean. It is home to approximately 75% of the world's active and dormant volcanoes and is responsible for around 90% of the world's earthquakes. This zone is formed by the interaction of several tectonic plates, including the Pacific Plate, the North American Plate, and the Philippine Sea Plate. Countries like Japan, New Zealand, and the western coast of South America are part of this highly active region.
The Alpine-Himalayan Belt

The Alpine-Himalayan Belt is another seismically active region, stretching from the Mediterranean Sea to the Indian subcontinent. This belt is formed by the collision of the African, Arabian, and Indian plates with the Eurasian Plate. The result is a series of mountain ranges, including the Alps and the Himalayas. Earthquakes in this region can be quite destructive, as seen in the 2005 Kashmir earthquake in Pakistan, which killed over 80,000 people.
Mid-Atlantic Ridge

The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a divergent boundary that runs down the center of the Atlantic Ocean. Here, the Eurasian and North American plates are moving away from each other, allowing molten rock to rise and form new oceanic crust. While earthquakes in this region are less frequent than in other parts of the world, they can still occur, as seen in the 1929 Grand Banks earthquake off the coast of Newfoundland, which triggered a significant tsunami.
Earthquakes and Human Settlements
Earthquakes can have devastating impacts on human settlements, especially in regions with high population densities and inadequate building standards. The destruction caused by earthquakes can lead to loss of life, injuries, and extensive damage to infrastructure. Some of the most devastating earthquakes in recent history include the 2010 Haiti earthquake, the 2008 Sichuan earthquake in China, and the 1999 İzmit earthquake in Turkey.
Preparation and Mitigation
In areas prone to earthquakes, it is crucial to have proper building codes and disaster preparedness plans in place. Structures should be designed to withstand seismic activity, and regular drills should be conducted to ensure that residents know how to respond during an earthquake. Early warning systems can also provide valuable time for people to seek safety before the shaking begins.
Earthquake Prediction and Research

While it is currently impossible to predict exactly when and where an earthquake will occur, scientists are constantly working to improve their understanding of these natural phenomena. Through advanced technology and research, they aim to develop better prediction models and early warning systems. Additionally, studying past earthquakes helps scientists identify patterns and improve their understanding of the Earth's interior.
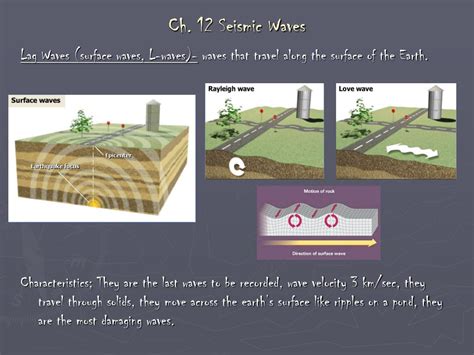
Seismic Monitoring

Seismic monitoring stations are crucial for detecting and analyzing earthquakes. These stations use sensitive instruments called seismometers to record ground motion. By studying the data collected from these stations, scientists can determine the location, magnitude, and depth of an earthquake. This information is vital for issuing timely warnings and assessing the potential impact of an earthquake.
Earthquake Early Warning Systems

Earthquake early warning systems are being developed and implemented in various parts of the world. These systems use real-time data from seismic monitoring stations to detect an earthquake's initial P-waves, which travel faster than the more destructive S-waves. By analyzing the P-waves, the system can provide a few seconds to minutes of warning before the arrival of the S-waves, allowing people to take cover or evacuate vulnerable areas.
Conclusion

Earthquakes are a natural part of our planet's geology, and they can occur in various regions around the world. Understanding the different types of tectonic plate interactions and the associated seismic activity is crucial for preparing and mitigating the impacts of these events. By investing in research, improving building standards, and implementing early warning systems, we can work towards minimizing the loss of life and property caused by earthquakes.
What causes earthquakes to occur in specific regions?

+
Earthquakes occur in specific regions due to the movement and interaction of tectonic plates. When plates collide, slide past each other, or move apart, it can lead to the release of energy, resulting in earthquakes. These plate boundaries are often found in regions like the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Alpine-Himalayan Belt, and divergent boundaries like the Mid-Atlantic Ridge.
Can earthquakes occur in areas with no volcanic activity?
+Yes, earthquakes can occur in areas with no volcanic activity. While volcanic regions are often associated with high seismic activity due to the movement of magma and the release of gases, earthquakes can also happen in areas where there is no volcanic presence. This is because earthquakes are primarily caused by the movement of tectonic plates, which can occur in various parts of the Earth’s crust.
Are there any warning signs before an earthquake occurs?
+While there are no definitive warning signs, scientists have identified certain precursory phenomena that may indicate an impending earthquake. These include changes in groundwater levels, the appearance of new cracks in the Earth’s surface, and the detection of unusual animal behavior. However, these signs are not always present, and their interpretation can be challenging.
How can we prepare for earthquakes?
+Preparing for earthquakes involves a combination of measures. This includes ensuring that buildings and infrastructure are constructed to withstand seismic activity, conducting regular earthquake drills, and having emergency supplies readily available. It is also crucial to stay informed about local early warning systems and evacuation plans.
Can earthquakes be prevented?
+No, earthquakes cannot be prevented as they are natural occurrences resulting from the movement of tectonic plates. However, through scientific research, early warning systems, and improved building practices, we can minimize the impact and reduce the loss of life and property caused by earthquakes.

