What Is Warrant Officer


Introduction to Warrant Officers
A warrant officer is a technical expert in a specific area, holding a unique position in the military hierarchy. They are highly skilled and experienced individuals who have risen through the ranks, demonstrating exceptional proficiency in their field. Warrant officers serve as mentors, instructors, and advisors, providing critical support to commanders and other personnel. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of warrant officers, exploring their roles, responsibilities, and the paths they take to achieve this esteemed position.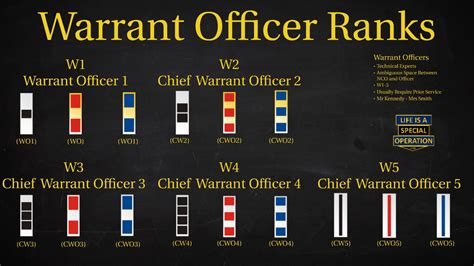
History of Warrant Officers
The concept of warrant officers dates back to the 13th century, when the British Royal Navy employed warrant officers as technical specialists. These individuals were responsible for maintaining and operating the ship’s systems, including navigation, engineering, and armament. The practice soon spread to other branches of the military, with each adopting its own version of the warrant officer system. Today, warrant officers can be found in various military forces around the world, serving in a range of roles, from technical experts to leaders and advisors.
Roles and Responsibilities
Warrant officers are technical experts in their field, responsible for providing guidance and support to commanders and other personnel. Their roles and responsibilities vary depending on their area of specialization, but common duties include: * Providing technical advice and guidance to commanders and other personnel * Developing and implementing training programs to enhance unit capabilities * Conducting inspections and evaluations to ensure compliance with standards and regulations * Serving as mentors and instructors, helping to develop the skills of junior personnel * Participating in planning and decision-making processes, providing technical expertise to inform command decisions
Paths to Becoming a Warrant Officer
The path to becoming a warrant officer varies depending on the country and branch of service. In general, individuals must meet certain eligibility requirements, including: * Completion of basic training and advanced individual training * Achievement of a certain rank or level of experience * Completion of a warrant officer candidate course or equivalent training * Possession of specialized skills and knowledge in a specific area Some common paths to becoming a warrant officer include: * Enlisted to Warrant Officer: Individuals who have served in the enlisted ranks may be eligible to apply for warrant officer candidacy, provided they meet the necessary requirements. * Direct Commission: In some cases, individuals with specialized skills and experience may be directly commissioned as warrant officers, bypassing the traditional enlisted route. * Lateral Entry: Some military forces allow individuals to lateral entry into the warrant officer corps, provided they have relevant experience and qualifications.
Types of Warrant Officers
There are several types of warrant officers, each with its own area of specialization. Some common examples include: * Aviation Warrant Officers: Experts in aviation maintenance, repair, and operation * Intelligence Warrant Officers: Specialists in intelligence gathering, analysis, and dissemination * Cyber Warrant Officers: Experts in cyber operations, security, and defense * Logistics Warrant Officers: Specialists in supply chain management, transportation, and maintenance
Benefits and Challenges
Serving as a warrant officer comes with numerous benefits, including: * Career Advancement: Warrant officers have opportunities for career advancement and professional growth * Increased Pay and Benefits: Warrant officers receive higher pay and benefits compared to their enlisted counterparts * Leadership Opportunities: Warrant officers have opportunities to lead and mentor junior personnel However, the role also presents challenges, such as: * High Expectations: Warrant officers are expected to maintain high levels of proficiency and expertise * Increased Responsibility: Warrant officers often bear significant responsibility for the success of their units * Continuous Learning: Warrant officers must stay up-to-date with the latest developments in their field, requiring continuous learning and professional development📝 Note: Warrant officers play a critical role in the military, providing technical expertise and leadership to support unit operations. Their unique blend of technical knowledge and leadership skills makes them an invaluable asset to military forces around the world.

Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, warrant officers are highly skilled and experienced individuals who play a vital role in the military. Their technical expertise, leadership skills, and mentorship make them an essential part of military operations. As the military continues to evolve and adapt to new challenges, the importance of warrant officers will only continue to grow. Whether serving in a technical, leadership, or advisory capacity, warrant officers are truly the backbone of the military, providing critical support to commanders and personnel alike.
What is the role of a warrant officer in the military?
+A warrant officer is a technical expert in a specific area, responsible for providing guidance and support to commanders and other personnel. They serve as mentors, instructors, and advisors, providing critical support to unit operations.

How do I become a warrant officer?
+The path to becoming a warrant officer varies depending on the country and branch of service. Typically, individuals must meet certain eligibility requirements, including completion of basic training and advanced individual training, achievement of a certain rank or level of experience, and possession of specialized skills and knowledge in a specific area.

What are the benefits of serving as a warrant officer?
+Serving as a warrant officer comes with numerous benefits, including career advancement, increased pay and benefits, and leadership opportunities. Warrant officers also have the opportunity to make a meaningful impact on unit operations and contribute to the development of junior personnel.



