What Is An Experimental Variable
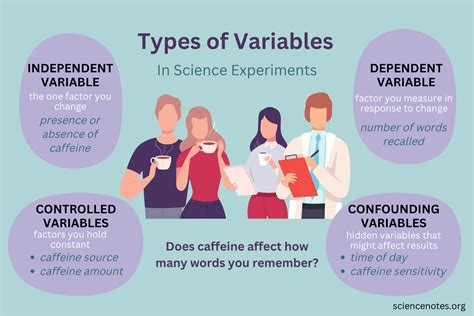
In the realm of scientific research and experiments, understanding the different types of variables is crucial for designing and interpreting studies accurately. Among these variables, the experimental variable stands out as a fundamental concept. This blog post aims to delve into the world of experimental variables, exploring their definition, role, and significance in scientific investigations.
Understanding Experimental Variables

An experimental variable, often referred to as the independent variable, is a crucial element in scientific experiments. It represents the factor that researchers manipulate or control to observe its effect on another variable, known as the dependent variable. In simpler terms, the experimental variable is the variable that scientists intentionally change to study its impact on the outcome of an experiment.
By systematically altering the experimental variable, researchers can gather valuable data and draw meaningful conclusions about cause-and-effect relationships. This approach allows them to determine how changes in the independent variable influence the dependent variable, providing insights into the underlying mechanisms and phenomena being studied.
The Role of Experimental Variables

Experimental variables play a pivotal role in scientific research for several reasons:
- Causal Inference: By manipulating the experimental variable, researchers can establish a cause-and-effect relationship between it and the dependent variable. This enables them to make predictions and draw conclusions about the impact of changes in the independent variable on the outcome.
- Control and Replication: Experimental variables allow researchers to control and replicate experimental conditions. By keeping all other variables constant, they can isolate the effect of the independent variable, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of their findings.
- Data Analysis: The data collected from experiments involving experimental variables provide a basis for statistical analysis. Researchers can employ various statistical techniques to analyze the relationship between the independent and dependent variables, drawing meaningful insights from the data.
Types of Experimental Variables
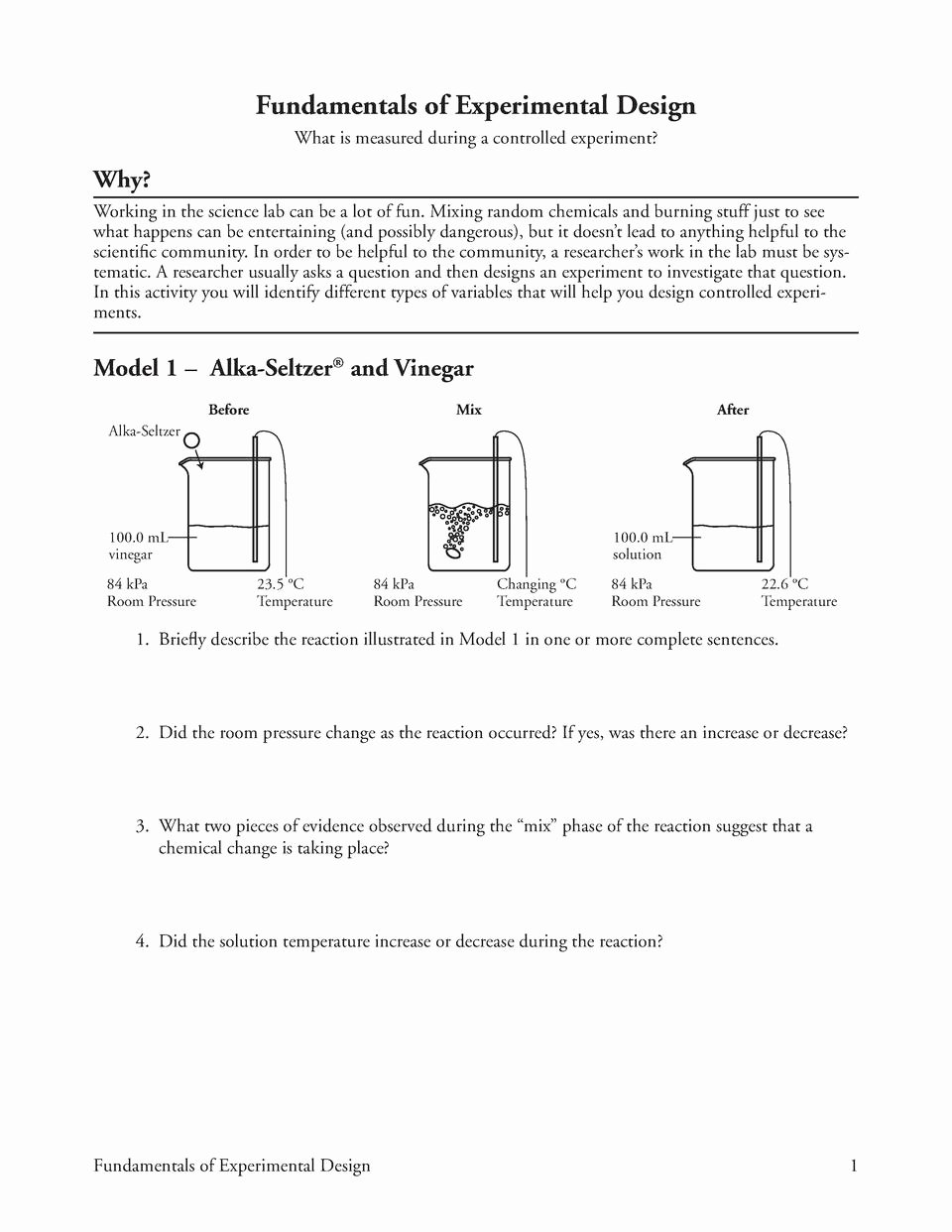
Experimental variables can be categorized into different types based on their nature and how they are manipulated:
- Continuous Variables: These variables can take on any value within a range. For example, temperature, time, or distance are continuous variables as they can have an infinite number of values.
- Categorical Variables: Also known as qualitative variables, these represent categories or groups. Examples include gender, color, or treatment type, where the data falls into distinct, non-numeric categories.
- Quantitative Variables: Quantitative variables are numerical and represent measurable quantities. Examples include height, weight, or test scores, where the data is represented by numerical values.
- Discrete Variables: Discrete variables can only take on specific, countable values. Examples include the number of siblings, the number of days in a week, or the number of students in a class.
Identifying Experimental Variables

When designing an experiment, it is essential to clearly identify the experimental variable. This involves asking questions such as:
- What factor do I want to manipulate or control in the experiment?
- What variable do I expect to have an impact on the outcome of the experiment?
- How can I systematically vary the experimental variable to observe its effect on the dependent variable?
By answering these questions, researchers can define the experimental variable and develop a well-structured experimental design.
Examples of Experimental Variables

To illustrate the concept of experimental variables, let's consider a few examples:
- In a study investigating the effect of different lighting conditions on plant growth, the experimental variable would be the type of light (e.g., fluorescent, LED, or natural sunlight) used to illuminate the plants.
- When researching the impact of exercise intensity on cardiovascular fitness, the experimental variable would be the intensity level of the exercise routine (e.g., low, moderate, or high-intensity workouts).
- In a medical trial evaluating the effectiveness of a new drug, the experimental variable would be the dosage or concentration of the drug administered to the participants.
Control Variables and Experimental Design

While the experimental variable is the focus of manipulation, it is important to consider control variables as well. Control variables are factors that researchers keep constant or minimize their variation to ensure that only the experimental variable influences the outcome. By controlling these variables, researchers can isolate the effect of the independent variable and avoid confounding factors that may affect the results.
A well-designed experimental setup should carefully consider both the experimental and control variables to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings. This involves selecting appropriate control groups, randomizing the assignment of participants or subjects, and employing statistical techniques to analyze the data.
Conclusion

In conclusion, experimental variables are a cornerstone of scientific research, allowing researchers to investigate cause-and-effect relationships and draw meaningful conclusions. By manipulating the experimental variable, scientists can gain insights into how changes in one factor influence another. Understanding the role and types of experimental variables is essential for designing robust experiments and advancing our knowledge in various scientific disciplines.
What is the difference between an experimental variable and a control variable?

+
An experimental variable is the factor that researchers manipulate to observe its effect, while a control variable is kept constant to minimize its impact on the outcome.
How do experimental variables contribute to scientific progress?

+
Experimental variables enable researchers to establish cause-and-effect relationships, which is crucial for developing theories, testing hypotheses, and advancing scientific understanding.
Can an experiment have multiple experimental variables?

+
Yes, in some complex experiments, researchers may manipulate multiple experimental variables simultaneously to study their combined effects.

