What Are Bank Reserves


Understanding Bank Reserves
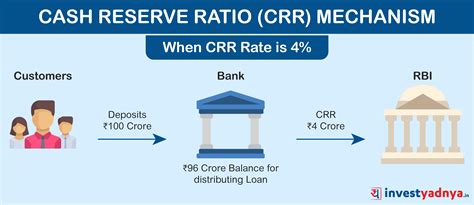
Bank reserves refer to the minimum amount of cash and other liquid assets that a bank is required to hold in its vaults or at the central bank, rather than lending them out to customers. The main purpose of bank reserves is to ensure that banks have sufficient funds to meet their short-term obligations, such as withdrawals by depositors. In this article, we will delve into the world of bank reserves, exploring their importance, types, and impact on the economy.
Importance of Bank Reserves
Bank reserves play a crucial role in maintaining the stability of the financial system. By holding a certain percentage of deposits in reserve, banks can:- Ensure liquidity: Bank reserves enable banks to meet unexpected withdrawals or other liquidity needs, preventing a bank run and maintaining confidence in the banking system.
- Manage risk: By holding a buffer of reserves, banks can absorb potential losses or shocks, reducing the risk of insolvency and protecting depositors’ funds.
- Implement monetary policy: Central banks use reserve requirements as a tool to influence the money supply and control inflation, as changes in reserve requirements can affect the amount of credit available in the economy.
Types of Bank Reserves
There are two main types of bank reserves:- Required reserves: These are the minimum reserves that a bank is required to hold against its deposit liabilities, as specified by the central bank or regulatory authority.
- Excess reserves: These are reserves held by a bank in excess of the required reserve ratio, which can be used to make loans or invest in other assets.

How Bank Reserves Work
The process of holding and using bank reserves involves the following steps:- Deposits: Customers deposit funds into their bank accounts, increasing the bank’s deposit liabilities.
- Reserve requirements: The bank must set aside a portion of these deposits as required reserves, based on the reserve requirement ratio.
- Lending: The bank can lend out the remaining funds (excess reserves) to other customers, creating new deposits and expanding the money supply.
- Reserve maintenance: The bank must continuously monitor its reserve position and adjust its lending or deposit-taking activities to maintain the required reserve ratio.
📝 Note: The reserve requirement ratio can vary depending on the country, type of deposit, and other factors, so it's essential to understand the specific regulations and requirements in your jurisdiction.

Impact of Bank Reserves on the Economy
Changes in bank reserves can have significant effects on the economy, including:- Money supply: An increase in bank reserves can lead to an expansion of the money supply, as banks lend out more funds and create new deposits.
- Interest rates: Changes in reserve requirements can influence interest rates, as banks adjust their lending rates in response to changes in the reserve requirement ratio.
- Banking stability: A well-managed reserve system helps maintain confidence in the banking system, reducing the risk of bank runs and financial crises.

| Reserve Requirement Ratio | Money Supply | Interest Rates |
|---|---|---|
| 10% | Expansion | Lower |
| 20% | Contraction | Higher |
In conclusion, bank reserves are a vital component of the financial system, providing a buffer against potential losses and enabling banks to meet their short-term obligations. Understanding the importance, types, and impact of bank reserves is essential for maintaining a stable and efficient banking system.
To summarize, the key points of this article are: * Bank reserves are the minimum amount of cash and other liquid assets that a bank must hold in its vaults or at the central bank. * Bank reserves play a crucial role in ensuring liquidity, managing risk, and implementing monetary policy. * There are two main types of bank reserves: required reserves and excess reserves. * Changes in bank reserves can have significant effects on the economy, including the money supply, interest rates, and banking stability.

What is the purpose of bank reserves?
+The purpose of bank reserves is to ensure that banks have sufficient funds to meet their short-term obligations, such as withdrawals by depositors, and to maintain the stability of the financial system.

How do changes in reserve requirements affect the economy?
+Changes in reserve requirements can influence the money supply, interest rates, and banking stability, as banks adjust their lending and deposit-taking activities in response to changes in the reserve requirement ratio.

What are the different types of bank reserves?
+There are two main types of bank reserves: required reserves, which are the minimum reserves that a bank is required to hold against its deposit liabilities, and excess reserves, which are reserves held by a bank in excess of the required reserve ratio.