Us Military Pay Raise
Introduction to US Military Pay Raise
The US military pay raise is an annual increase in the basic pay for members of the US Armed Forces, including the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, and Coast Guard. The pay raise is determined by the US Congress and is typically based on the Economic Growth Rate and the Employment Cost Index. The pay raise is designed to keep pace with the rising cost of living and to ensure that military personnel receive a fair and competitive salary for their service.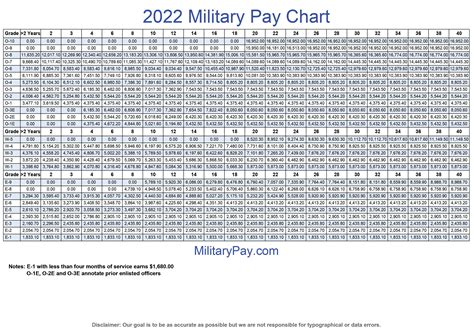
History of US Military Pay Raise
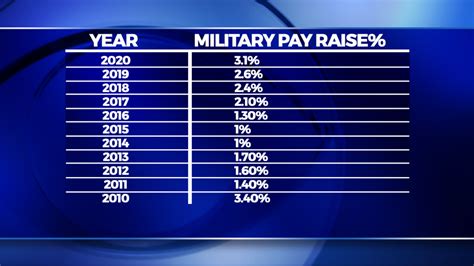
The US military pay raise has a long history, dating back to the early 20th century. Prior to 1920, military pay was not adjusted regularly, and it was not until the Pay Readjustment Act of 1920 that the US Congress established a system for regular pay increases. Since then, the pay raise has been adjusted annually, with some exceptions during times of economic downturn or war. Over the years, the pay raise has ranged from a low of 0% in 2011 to a high of 14.1% in 1981.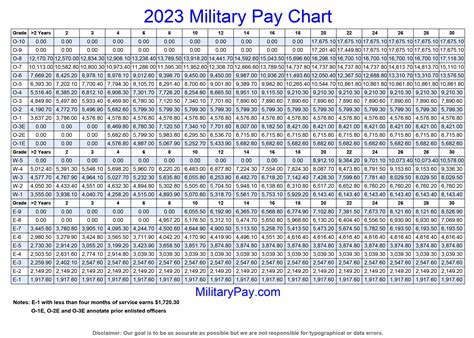
How US Military Pay Raise is Determined
The US military pay raise is determined by the US Congress, which takes into account various factors, including: * Economic Growth Rate: The rate at which the US economy is growing, as measured by the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). * Employment Cost Index: A measure of the rate of change in labor costs, including wages and benefits. * Private Sector Pay: The rate of pay increases in the private sector, as measured by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. * Military Recruitment and Retention: The ability of the military to recruit and retain personnel, which can be affected by pay and benefits. The US Congress uses these factors to determine the pay raise, which is typically announced in January of each year.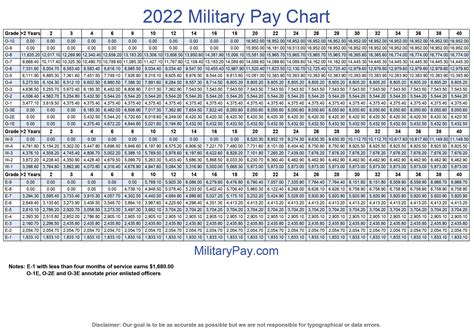
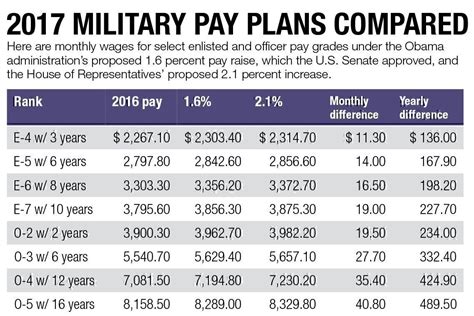
US Military Pay Raise Rates
The US military pay raise rates have varied over the years, with some years seeing higher increases than others. Here are some recent pay raise rates: * 2022: 2.7% * 2021: 3.0% * 2020: 3.1% * 2019: 2.6% * 2018: 2.4% The pay raise rate is applied to the basic pay of all military personnel, regardless of rank or branch of service.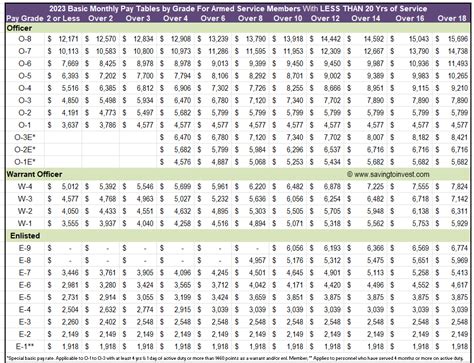
Impact of US Military Pay Raise
The US military pay raise has a significant impact on military personnel and their families. A pay raise can: * Increase take-home pay, allowing military personnel to better support themselves and their families. * Improve recruitment and retention, as higher pay can make military service more attractive to potential recruits. * Enhance morale and job satisfaction, as military personnel feel that their service is valued and recognized. * Support national security, by ensuring that the US military has the resources it needs to defend the country and its interests.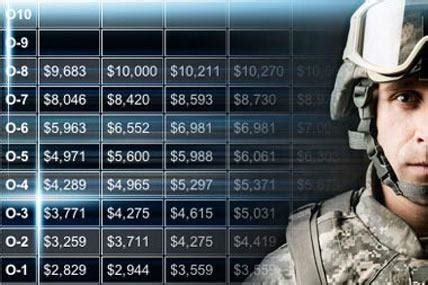
US Military Pay Raise and Benefits
In addition to basic pay, military personnel also receive a range of benefits, including: * Allowances: Special pay for things like housing, food, and clothing. * Bonuses: One-time payments for things like enlistment, reenlistment, and special skills. * Healthcare: Comprehensive medical and dental coverage for military personnel and their families. * Education Assistance: Financial assistance for education and training, including the GI Bill. These benefits can significantly enhance the overall compensation package for military personnel, and can help to offset the challenges and risks of military service.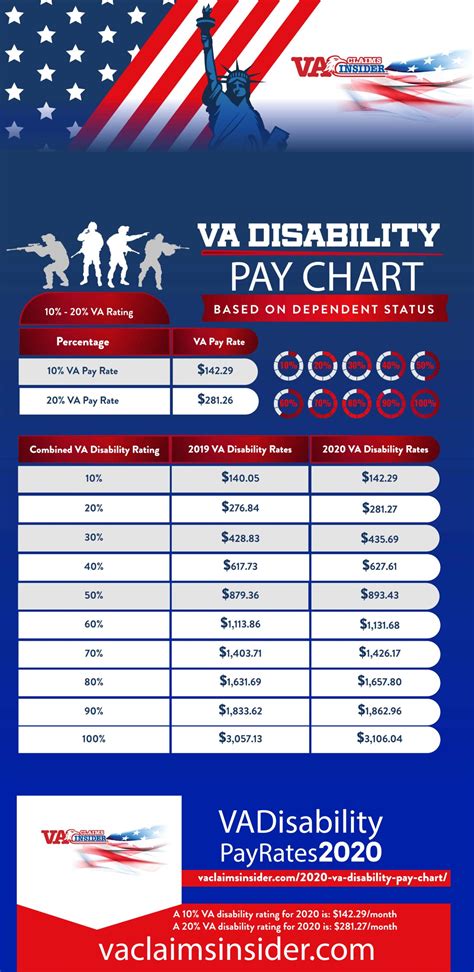
| Rank | Basic Pay (2022) | Basic Pay (2021) |
|---|---|---|
| Private (E-1) | $1,733.40 | $1,733.40 |
| Private First Class (E-2) | $1,942.50 | $1,942.50 |
| Specialist/Corporal (E-4) | $2,515.70 | $2,515.70 |
| Sergeant (E-5) | $3,075.90 | $3,075.90 |
| Staff Sergeant (E-6) | $3,756.30 | $3,756.30 |
📝 Note: The pay rates listed in the table are for the US Army, and may vary depending on the branch of service and other factors.
In summary, the US military pay raise is an important aspect of military compensation, and is designed to keep pace with the rising cost of living and to ensure that military personnel receive a fair and competitive salary for their service. The pay raise is determined by the US Congress, which takes into account various factors, including economic growth, employment costs, and private sector pay. The pay raise has a significant impact on military personnel and their families, and can improve recruitment and retention, morale and job satisfaction, and national security.
The US military pay raise is a critical component of the overall compensation package for military personnel, which includes basic pay, allowances, bonuses, healthcare, and education assistance. The pay raise is typically announced in January of each year, and is applied to the basic pay of all military personnel, regardless of rank or branch of service. By understanding the US military pay raise and its impact on military personnel, we can better appreciate the sacrifices and challenges of military service, and the importance of supporting those who serve our country.
To get the most out of the US military pay raise, military personnel should: * Stay informed about pay raise rates and changes to the compensation package. * Take advantage of benefits like allowances, bonuses, and education assistance. * Plan carefully for the future, including saving for retirement and investing in education and training. * Seek support from military resources, like financial counseling and career guidance.
By following these tips, military personnel can make the most of the US military pay raise, and can achieve financial stability and security, both during and after their military service.

How is the US military pay raise determined?
+The US military pay raise is determined by the US Congress, which takes into account various factors, including economic growth, employment costs, and private sector pay.

What is the average US military pay raise rate?
+The average US military pay raise rate varies from year to year, but it is typically around 2-3%.

How does the US military pay raise affect military personnel?
+The US military pay raise can have a significant impact on military personnel, improving their take-home pay, recruitment and retention, morale and job satisfaction, and national security.



