Us Army Rank Structure

Introduction to the US Army Rank Structure
The US Army rank structure is a system of hierarchical ranks and positions that define an individual’s level of authority, responsibility, and pay grade within the Army. The rank structure is designed to provide a clear chain of command and to recognize an individual’s level of experience, skills, and accomplishments. In this article, we will explore the different ranks within the US Army, from the lowest to the highest, and provide an overview of the responsibilities and requirements associated with each rank.
Enlisted Ranks
The enlisted ranks are the foundation of the US Army and are divided into nine ranks, each with its own set of responsibilities and requirements. The enlisted ranks are: * Private (PVT) - The lowest rank in the Army, privates are typically new recruits who are still in training. * Private Second Class (PV2) - Privates second class have completed basic training and are assigned to a unit. * Private First Class (PFC) - Private first class are experienced soldiers who have demonstrated leadership potential. * Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) - Specialists and corporals are technical experts in their field and are responsible for leading small teams. * Sergeant (SGT) - Sergeants are experienced leaders who are responsible for leading squads and sections. * Staff Sergeant (SSG) - Staff sergeants are senior leaders who are responsible for leading platoons and companies. * Sergeant First Class (SFC) - Sergeant first class are senior enlisted leaders who are responsible for leading battalions and brigades. * Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG) - Master sergeants and first sergeants are senior leaders who are responsible for leading large units and providing guidance and mentorship to junior soldiers. * Sergeant Major (SGM) - Sergeant majors are the highest-ranking enlisted soldiers in the Army and serve as senior advisors to commanders.
Warrant Officer Ranks
Warrant officers are technical experts who have advanced education and training in a specific field. They are responsible for providing technical guidance and advice to commanders and are typically assigned to specialty positions such as pilots, intelligence analysts, and communications specialists. The warrant officer ranks are: * Warrant Officer 1 (WO1) - Warrant officer 1 is the lowest rank in the warrant officer corps and is typically assigned to junior positions. * Chief Warrant Officer 2 (CW2) - Chief warrant officer 2 are experienced warrant officers who have demonstrated technical expertise and leadership potential. * Chief Warrant Officer 3 (CW3) - Chief warrant officer 3 are senior warrant officers who are responsible for leading teams and providing technical guidance to commanders. * Chief Warrant Officer 4 (CW4) - Chief warrant officer 4 are senior leaders who are responsible for leading large units and providing technical expertise to commanders. * Chief Warrant Officer 5 (CW5) - Chief warrant officer 5 is the highest rank in the warrant officer corps and is typically assigned to senior positions such as command chief warrant officer.
Officer Ranks
Officer ranks are divided into three categories: company grade, field grade, and general officer. Company grade officers are typically assigned to junior positions and are responsible for leading small units. Field grade officers are senior leaders who are responsible for leading large units and providing guidance and mentorship to junior officers. General officers are the highest-ranking officers in the Army and are responsible for leading major commands and developing strategy. * Second Lieutenant (2LT) - Second lieutenant is the lowest rank in the officer corps and is typically assigned to junior positions. * First Lieutenant (1LT) - First lieutenant are experienced officers who have demonstrated leadership potential. * Captain (CPT) - Captains are company grade officers who are responsible for leading companies and batteries. * Major (MAJ) - Majors are field grade officers who are responsible for leading battalions and brigades. * Lieutenant Colonel (LTC) - Lieutenant colonels are senior field grade officers who are responsible for leading large units and providing guidance and mentorship to junior officers. * Colonel (COL) - Colonels are senior leaders who are responsible for leading brigades and divisions. * Brigadier General (BG) - Brigadier generals are one-star generals who are responsible for leading large units and developing strategy. * Major General (MG) - Major generals are two-star generals who are responsible for leading divisions and corps. * Lieutenant General (LTG) - Lieutenant generals are three-star generals who are responsible for leading large commands and developing strategy. * General (GEN) - General is the highest rank in the Army and is typically assigned to senior positions such as Chief of Staff.👮 Note: The US Army rank structure is subject to change, and individual ranks and responsibilities may vary depending on the specific unit and mission.
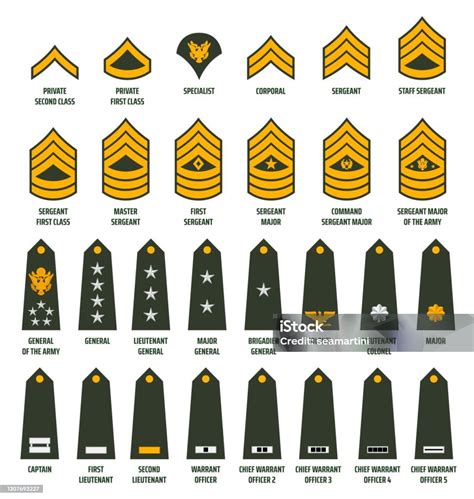

Rank Insignia
Rank insignia are the symbols and emblems that are worn on a soldier’s uniform to indicate their rank. The US Army uses a system of chevrons, stripes, and stars to indicate rank. Enlisted ranks are indicated by chevrons, while officer ranks are indicated by stripes and stars. Warrant officer ranks are indicated by a unique insignia that is a combination of chevrons and stripes.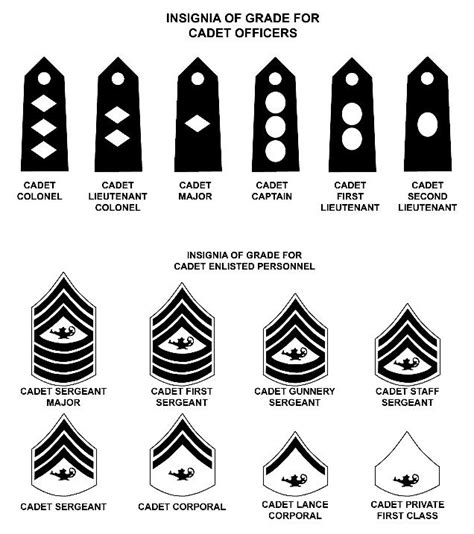
| Rank | Insignia |
|---|---|
| Private (PVT) | No insignia |
| Private Second Class (PV2) | One chevron |
| Private First Class (PFC) | One chevron with a rocker |
| Specialist/Corporal (SPC/CPL) | Two chevrons |
| Sergeant (SGT) | Three chevrons |
| Staff Sergeant (SSG) | Three chevrons with a rocker |
| Sergeant First Class (SFC) | Three chevrons with two rockers |
| Master Sergeant/First Sergeant (MSG/1SG) | Three chevrons with three rockers |
| Sergeant Major (SGM) | Three chevrons with four rockers |
| Second Lieutenant (2LT) | One gold bar |
| First Lieutenant (1LT) | One silver bar |
| Captain (CPT) | Two silver bars |
| Major (MAJ) | One gold oak leaf |
| Lieutenant Colonel (LTC) | One silver oak leaf |
| Colonel (COL) | One gold eagle |
| Brigadier General (BG) | One star |
| Major General (MG) | Two stars |
| Lieutenant General (LTG) | Three stars |
| General (GEN) | Four stars |
In summary, the US Army rank structure is a complex system of hierarchical ranks and positions that define an individual’s level of authority, responsibility, and pay grade. Understanding the different ranks and their responsibilities is essential for navigating the Army’s chain of command and for developing a successful military career. By recognizing the achievements and contributions of individual soldiers, the US Army rank structure provides a framework for promoting excellence and leadership within the military.
What is the lowest rank in the US Army?
+The lowest rank in the US Army is Private (PVT).
What is the highest rank in the US Army?
+The highest rank in the US Army is General (GEN).



