Step Up Converter Circuit
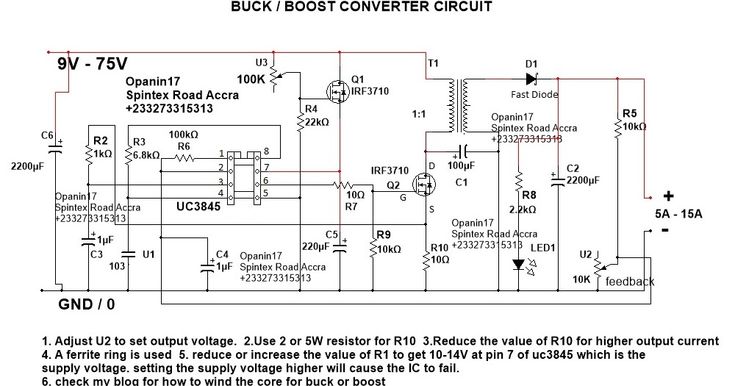
In the world of electronics, understanding the fundamentals of voltage conversion is crucial for various applications. One such fundamental circuit is the step-up converter, also known as a boost converter, which plays a vital role in increasing voltage levels efficiently. This blog post will delve into the workings of a step-up converter circuit, exploring its components, principles, and practical applications.
Understanding the Step-Up Converter Circuit

A step-up converter circuit, as the name suggests, is designed to boost or increase the voltage level of a power source. It accomplishes this by converting a lower input voltage into a higher output voltage. This circuit finds its utility in numerous electronic devices and systems where a higher voltage is required for proper functioning.
Key Components of a Step-Up Converter

To comprehend the inner workings of a step-up converter, let's take a closer look at its essential components:
- Input Voltage Source: The input voltage source provides the initial voltage that needs to be stepped up. This can be a battery, solar panel, or any other suitable power source.
- Inductor: The inductor is a critical component in a step-up converter. It stores energy in the form of a magnetic field when the switch is closed and releases it when the switch is open. This energy storage and release mechanism is key to boosting the voltage.
- Switch: The switch, typically a transistor, controls the flow of current through the circuit. By rapidly turning the switch on and off, the energy is transferred to the output, resulting in a higher voltage.
- Diode: The diode, often a Schottky diode, prevents reverse current flow and ensures that the energy stored in the inductor is directed to the output smoothly.
- Output Capacitor: The output capacitor helps to smoothen out the voltage fluctuations and provides a stable output voltage. It stores excess energy during the on-state of the switch and releases it during the off-state, maintaining a consistent voltage level.
Working Principle of a Step-Up Converter

The operation of a step-up converter can be divided into two main phases: the on-state and the off-state of the switch.
On-State (Switch Closed)

- When the switch is closed, current flows through the inductor, creating a magnetic field around it.
- The energy stored in the inductor's magnetic field increases as the current flows.
- The diode prevents the current from flowing back to the input, directing it towards the output.
- The output capacitor charges up, storing energy for the off-state.
Off-State (Switch Open)

- When the switch opens, the current flow through the inductor is interrupted.
- The magnetic field around the inductor collapses, releasing the stored energy.
- This released energy is directed towards the output, boosting the voltage level.
- The output capacitor discharges, providing a stable output voltage during the off-state.
Practical Applications of Step-Up Converters

Step-up converters find widespread use in various electronic devices and systems. Here are some notable applications:
- LED Lighting: Step-up converters are commonly used in LED lighting systems to boost the voltage supplied to the LEDs, ensuring their optimal brightness.
- Solar Power Systems: In solar-powered applications, step-up converters help increase the voltage generated by solar panels, making it suitable for charging batteries or powering electronic devices.
- Motor Control: Step-up converters are utilized in motor control systems to provide the required voltage for efficient motor operation, especially in low-voltage scenarios.
- Battery-Powered Devices: Many battery-powered devices, such as laptops and smartphones, employ step-up converters to boost the voltage from the battery to meet the higher voltage requirements of their components.
- Power Supplies: Step-up converters are integral components in power supply units, ensuring that electronic devices receive the necessary voltage levels for their proper functioning.
Advantages of Step-Up Converters

Step-up converters offer several advantages, making them a popular choice in voltage conversion applications:
- High Efficiency: Step-up converters are known for their high efficiency, converting a significant portion of the input power into the desired output voltage.
- Compact Design: These converters can be designed with a small footprint, making them suitable for space-constrained applications.
- Wide Input Voltage Range: Step-up converters can handle a wide range of input voltages, making them versatile for various power sources.
- Stability: The use of an output capacitor ensures a stable and regulated output voltage, even during fluctuations in the input voltage.
Considerations and Limitations

While step-up converters offer numerous benefits, there are some considerations to keep in mind:
- Heat Generation: The rapid switching of the transistor can generate heat, which needs to be managed through proper heat sinking or cooling mechanisms.
- Noise and Electromagnetic Interference (EMI): The high-frequency switching can result in noise and EMI, which may require additional filtering or shielding.
- Component Selection: Choosing the right components, such as inductors and capacitors, is crucial to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
Designing a Step-Up Converter Circuit

Designing a step-up converter circuit involves several key steps:
- Determine Requirements: Start by defining the input voltage, desired output voltage, and the required current capacity.
- Component Selection: Select suitable components based on the requirements, considering factors like voltage ratings, current handling capacity, and efficiency.
- Calculate Inductor Value: The inductor value is crucial for energy storage and release. Calculate the required inductance using formulas or simulation tools.
- Switch Selection: Choose an appropriate switch, considering factors like switching speed, voltage and current ratings, and efficiency.
- Diode Selection: Select a diode with a low forward voltage drop and a high reverse voltage rating to minimize power loss and ensure proper operation.
- Output Capacitor: Determine the capacitance value to achieve the desired output voltage regulation and ripple reduction.
- Circuit Design: Create a schematic diagram and layout the circuit, ensuring proper component placement and wiring.
- Testing and Optimization: Test the circuit and make adjustments as needed to achieve the desired performance and efficiency.
It's important to note that designing a step-up converter circuit requires a good understanding of electronics and power conversion principles. Seeking guidance from experienced professionals or consulting relevant resources can be beneficial during the design process.
Safety Considerations

When working with step-up converters or any high-voltage circuits, safety should be a top priority. Here are some key safety considerations:
- High Voltage Hazards: Step-up converters can generate high voltages, which can be dangerous if not handled properly. Always follow safety protocols and use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when working with high-voltage circuits.
- Short Circuit Protection: Implement short circuit protection mechanisms to prevent damage to the circuit and connected devices in case of a short circuit.
- Overcurrent Protection: Incorporate overcurrent protection to safeguard the circuit and components from excessive current flow.
- Thermal Management: Ensure proper thermal management to prevent overheating of components. This can include heat sinks, cooling fans, or other cooling mechanisms.
Conclusion

Step-up converters are versatile and efficient circuits that play a crucial role in boosting voltage levels for various electronic applications. By understanding their components, working principles, and practical applications, designers and engineers can harness the power of step-up converters to meet the voltage requirements of their projects. Whether it's LED lighting, solar power systems, or motor control, step-up converters provide a reliable and efficient solution for voltage conversion needs.
What is the main purpose of a step-up converter circuit?

+
The primary purpose of a step-up converter circuit is to increase the voltage level of a power source, making it suitable for applications that require a higher voltage.
How does a step-up converter work?

+
A step-up converter works by storing energy in an inductor during the on-state of a switch and releasing it during the off-state, resulting in a higher output voltage.
What are some common applications of step-up converters?

+
Step-up converters are commonly used in LED lighting, solar power systems, motor control, and battery-powered devices, among other applications.
What factors should be considered when designing a step-up converter circuit?

+
When designing a step-up converter circuit, key factors to consider include input and output voltage requirements, current capacity, component selection, and thermal management.


