Sonography Tech Guide

Introduction to Sonography Technology
Sonography, also known as ultrasound, is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of structures within the body. The technology has become an essential tool in the medical field, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat various conditions. In this guide, we will delve into the world of sonography technology, exploring its principles, applications, and benefits.
Principles of Sonography
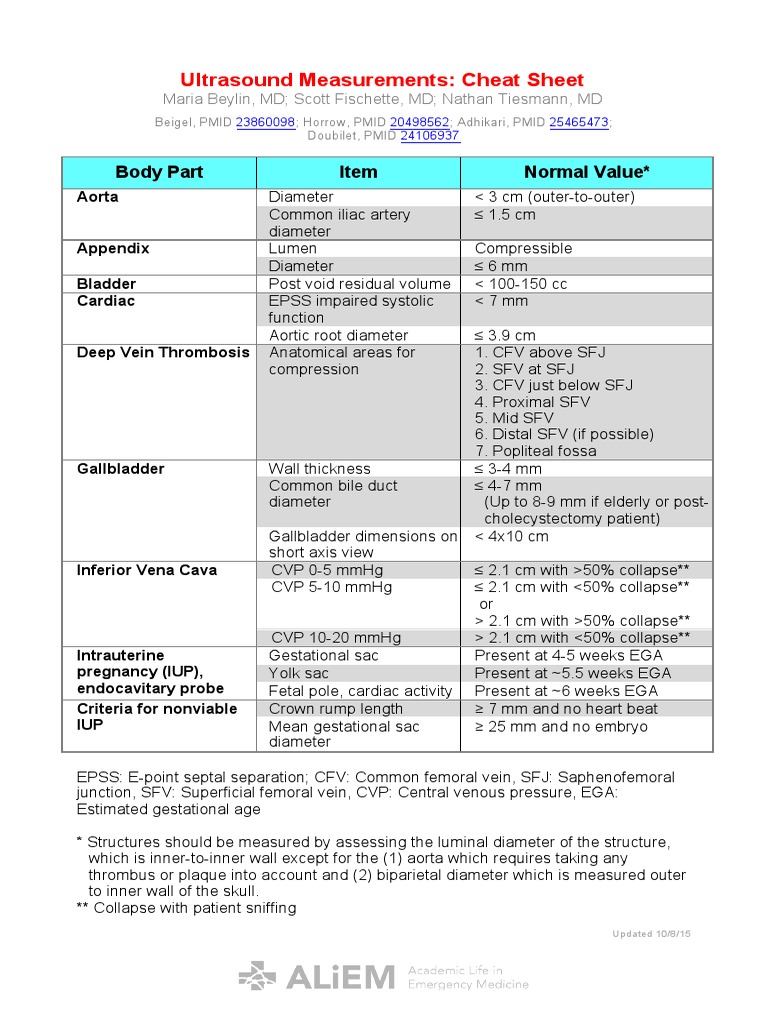
Sonography works on the principle of sound wave transmission and reflection. When a sound wave is transmitted into the body, it encounters different tissues and organs, which reflect the sound waves back to the transducer. The transducer then converts these reflected sound waves into electrical signals, which are processed to produce images on a screen. The frequency of the sound waves used in sonography ranges from 2 to 15 megahertz, which is beyond the range of human hearing.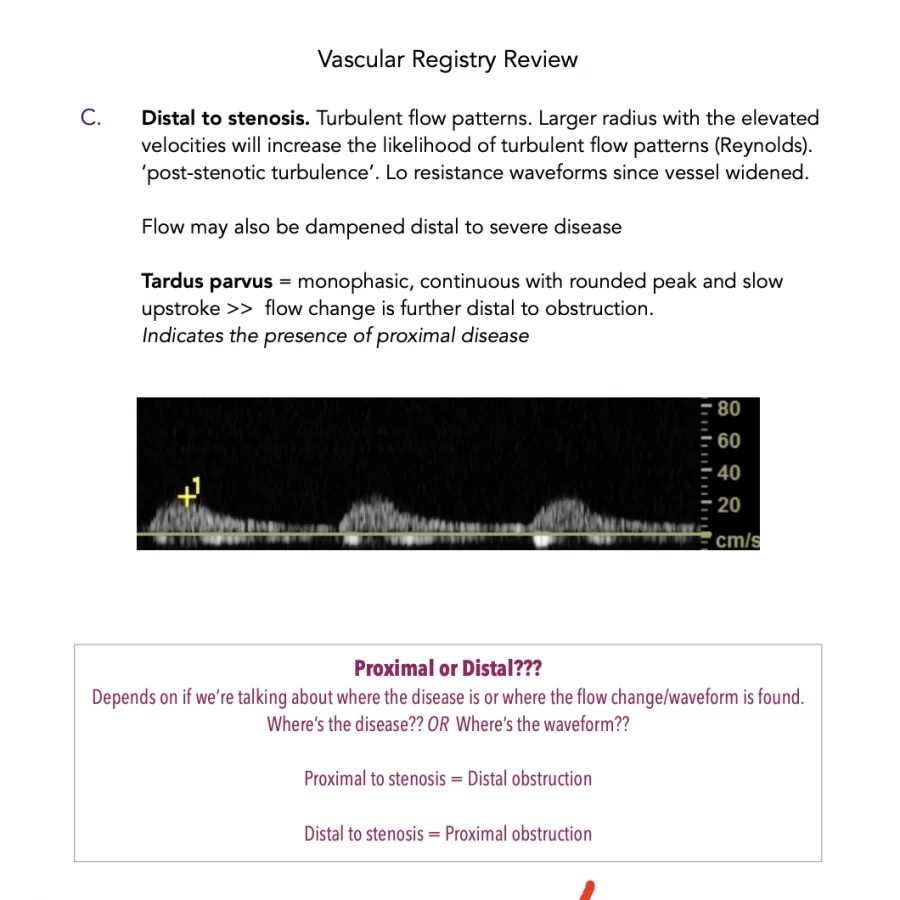
Types of Sonography
There are several types of sonography, each with its own specific application: * Diagnostic sonography: used to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions, such as pregnancy, gallstones, and liver disease. * Interventional sonography: used to guide minimally invasive procedures, such as biopsies and tumor treatments. * Cardiovascular sonography: used to diagnose and monitor heart and blood vessel conditions, such as heart disease and blood clots. * Musculoskeletal sonography: used to diagnose and monitor muscle and joint conditions, such as tendonitis and arthritis.
Benefits of Sonography
Sonography has several benefits that make it a popular medical imaging technique: * Non-invasive: sonography does not require the insertion of instruments or devices into the body, making it a safe and comfortable procedure for patients. * Low cost: sonography is generally less expensive than other medical imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans. * Real-time imaging: sonography allows for real-time imaging, enabling healthcare professionals to monitor procedures and diagnose conditions in real-time. * No radiation: sonography does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safe procedure for patients, especially pregnant women and children.
Applications of Sonography
Sonography has a wide range of applications in the medical field: * Pregnancy and obstetrics: sonography is used to monitor fetal development, detect potential complications, and guide procedures such as amniocentesis. * Abdominal and pelvic imaging: sonography is used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as gallstones, liver disease, and ovarian cysts. * Cardiovascular imaging: sonography is used to diagnose and monitor heart and blood vessel conditions, such as heart disease and blood clots. * Musculoskeletal imaging: sonography is used to diagnose and monitor muscle and joint conditions, such as tendonitis and arthritis.
Sonography Equipment and Techniques
Sonography equipment consists of a transducer, a processing unit, and a display screen. The transducer converts electrical signals into sound waves and receives reflected sound waves, which are then processed to produce images on the display screen. There are several sonography techniques, including: * 2D sonography: produces two-dimensional images of the body. * 3D sonography: produces three-dimensional images of the body. * Doppler sonography: measures blood flow and detects potential complications such as blood clots.
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| 2D sonography | Produces two-dimensional images of the body |
| 3D sonography | Produces three-dimensional images of the body |
| Doppler sonography | Measures blood flow and detects potential complications such as blood clots |
📝 Note: Sonography equipment and techniques are constantly evolving, with advances in technology leading to improved image quality and diagnostic accuracy.
Career Opportunities in Sonography
Sonography is a growing field, with increasing demand for skilled sonographers. Career opportunities in sonography include: * Diagnostic medical sonographer: performs sonography procedures and interprets images to diagnose medical conditions. * : performs sonography procedures and interprets images to diagnose heart and blood vessel conditions. * Musculoskeletal sonographer: performs sonography procedures and interprets images to diagnose muscle and joint conditions. * Sonography educator: teaches sonography techniques and principles to students and healthcare professionals.
Education and Training in Sonography
To become a sonographer, one must complete a formal education program in sonography, which typically includes: * Associate’s degree: a two-year program that includes classroom and clinical training. * Bachelor’s degree: a four-year program that includes advanced classroom and clinical training. * Certification: sonographers must obtain certification from a professional organization, such as the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS).In summary, sonography technology has revolutionized the medical field, providing a safe, non-invasive, and cost-effective means of diagnosing and monitoring various medical conditions. With its wide range of applications, sonography has become an essential tool in healthcare, and career opportunities in the field are growing. As technology continues to evolve, sonography will remain a vital component of medical imaging, enabling healthcare professionals to provide accurate diagnoses and effective treatments.

What is sonography used for?
+
Sonography is used to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions, such as pregnancy, gallstones, and liver disease.

Is sonography safe?
+
Yes, sonography is a safe and non-invasive medical imaging technique that does not use ionizing radiation.
What are the benefits of sonography?
+
The benefits of sonography include its non-invasive nature, low cost, real-time imaging, and lack of radiation.