Montgomery Vs Post 911


Introduction to the Montgomery Amendment and Post 911 GI Bill
The Montgomery GI Bill and the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill are two significant education benefits offered by the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) to eligible veterans, service members, and their families. While both programs share the common goal of providing financial assistance for education and training, they have distinct differences in terms of eligibility, benefits, and application processes. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of each program, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses, and discuss how they compare to each other.
Montgomery GI Bill
The Montgomery GI Bill (MGIB) was established in 1984 and is available to eligible service members who have contributed to the program through their military pay. There are two main categories under the MGIB: the Active Duty program (MGIB-AD) and the Selected Reserve program (MGIB-SR). To be eligible for the MGIB-AD, service members must have enlisted, re-enlisted, or extended their enlistment for a minimum of two years, and must have contributed $100 per month for the first 12 months of their military service. The MGIB-SR, on the other hand, is available to members of the Selected Reserve, which includes the Army Reserve, Navy Reserve, Air Force Reserve, Marine Corps Reserve, Coast Guard Reserve, and the Army National Guard and the Air National Guard.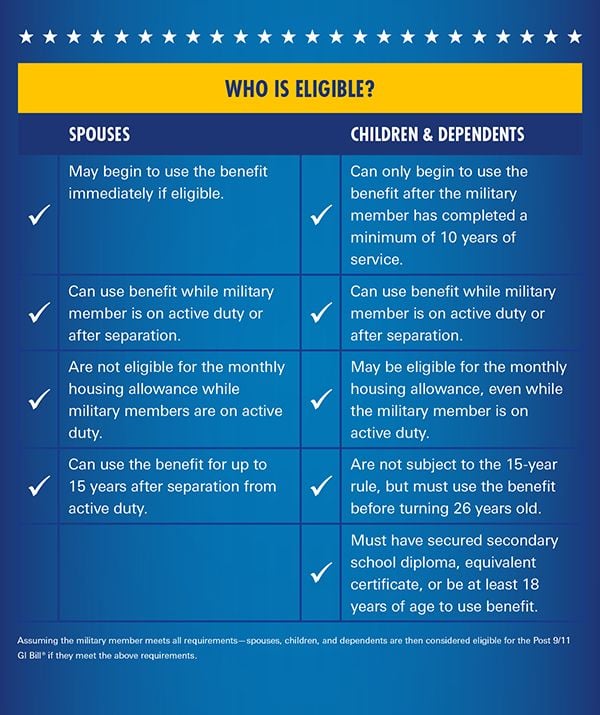
Post 911 GI Bill
The Post-9⁄11 GI Bill, also known as the Veterans Educational Assistance Act of 2008, was introduced to provide enhanced education benefits to veterans and service members who have served on active duty after September 10, 2001. This program is designed to cover more education expenses compared to the MGIB and offers a wider range of benefits, including tuition and fees, housing stipends, and book stipends. To be eligible for the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill, service members must have served at least 90 aggregate days of active duty after September 10, 2001, or have been discharged with a service-connected disability after serving at least 30 continuous days of active duty after September 10, 2001.
Comparison of Benefits
One of the main differences between the Montgomery GI Bill and the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill is the amount of education benefits provided. The MGIB typically offers a monthly benefit of up to 1,920 for full-time students, while the Post-9/11 GI Bill covers up to 100% of tuition and fees at public schools, and up to 25,162.14 per year at private schools. Additionally, the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill provides a monthly housing stipend and an annual book stipend of up to $1,000, which are not available under the MGIB.
Eligibility and Application Process
The eligibility and application processes for both programs also differ. For the MGIB, service members must have contributed to the program through their military pay, and must have an honorable discharge to be eligible. The application process involves submitting an application (VA Form 22-1990) to the VA, along with supporting documents such as discharge papers (DD Form 214) and transcripts. For the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill, service members must have served on active duty after September 10, 2001, and must have received an honorable discharge. The application process is similar to the MGIB, with service members submitting an application (VA Form 22-1990) and supporting documents.📝 Note: It's essential to review the eligibility requirements and application processes for both programs to determine which one is best suited for individual circumstances.

Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, both the Montgomery GI Bill and the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill offer valuable education benefits to eligible veterans, service members, and their families. While the MGIB provides a monthly benefit for education expenses, the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill offers more comprehensive benefits, including tuition and fees, housing stipends, and book stipends. As the VA continues to update and refine its education benefits programs, it’s crucial for individuals to stay informed about the latest developments and to carefully review their eligibility and options to make the most of these benefits.
What are the main differences between the Montgomery GI Bill and the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill?
+
The main differences between the two programs are the amount of education benefits provided, eligibility requirements, and application processes. The Post-9⁄11 GI Bill offers more comprehensive benefits, including tuition and fees, housing stipends, and book stipends, while the MGIB provides a monthly benefit for education expenses.

How do I apply for the Montgomery GI Bill or the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill?
+
To apply for either program, service members must submit an application (VA Form 22-1990) to the VA, along with supporting documents such as discharge papers (DD Form 214) and transcripts. It’s essential to review the eligibility requirements and application processes for both programs to determine which one is best suited for individual circumstances.

Can I use both the Montgomery GI Bill and the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill?
+
No, service members can only use one education benefits program at a time. However, in some cases, individuals may be eligible to switch from the MGIB to the Post-9⁄11 GI Bill, or vice versa, depending on their individual circumstances and eligibility.



