Military Academy Vs Enlisting


Introduction to Military Service
When considering a career in the military, there are generally two paths one can take: attending a military academy or enlisting. Both options offer a way to serve one’s country, but they differ significantly in terms of the experience, education, and future opportunities they provide. For those interested in pursuing a military career, understanding the distinctions between these two paths is crucial for making an informed decision.
Military Academy: An Overview
Attending a military academy is a prestigious and challenging way to begin a military career. These institutions, such as West Point, the Naval Academy, and the Air Force Academy, offer a four-year college education that is fully funded by the military in exchange for a commitment to serve as an officer upon graduation. The curriculum at these academies is rigorous and includes both academic studies and military training. Discipline, leadership, and physical fitness are highly valued, and cadets are expected to excel in all these areas. Upon graduation, academy attendees are commissioned as officers in their respective branches of the military.
Enlisting in the Military: An Alternative Path
Enlisting in the military involves signing up for a certain number of years of service as an enlisted member. This path does not require a college degree to start, although having one can offer advantages in terms of initial rank and specialty. Enlisted members undergo basic training, which teaches them the fundamentals of military life and their specific job skills. They have the opportunity to specialize in a wide range of fields, from combat roles to support positions like administration, healthcare, and technology. Promotions and career advancement in the enlisted ranks are based on performance, time in service, and passing certain exams.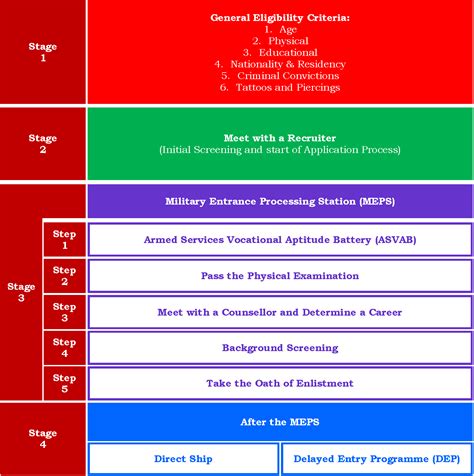
Key Differences: Academy vs. Enlisting
- Education: Military academies provide a free college education, while enlisting does not necessarily include education benefits, though the military offers tuition assistance and the GI Bill for those who want to pursue higher education. - Officer vs. Enlisted: Graduates of military academies become officers, while those who enlist start as enlisted members. Officers are leaders and managers, responsible for making strategic decisions, while enlisted members carry out the day-to-day tasks and operations. - Commitment: Both paths require a service commitment, but the terms can vary. Academy graduates typically owe 5 years of service as an officer, while enlistment contracts can range from 2 to 6 years, depending on the branch of service and the specific job chosen. - Lifestyle: The lifestyle as an officer versus an enlisted member can differ significantly, with officers often having more responsibilities and a more formal role within the military structure.
Choosing the Right Path
The decision between attending a military academy and enlisting should be based on individual goals, preferences, and circumstances. For those who value education and wish to enter the military as an officer, a military academy might be the better choice. On the other hand, for those who prefer to start serving immediately, gain practical skills, and have the opportunity to see if military life is a good fit before committing to a long-term education and service obligation, enlisting could be more appealing.📝 Note: It's essential to research thoroughly and consider visiting military bases or speaking with current or former military members to get a firsthand understanding of what each path entails.

Benefits and Drawbacks
Both attending a military academy and enlisting have their benefits and drawbacks. Benefits of attending an academy include a free education, automatic commission as an officer, and the prestige associated with graduating from a service academy. However, the process of getting accepted is highly competitive, and the academic and military rigors are demanding. Enlisting offers the opportunity to serve one’s country, gain valuable job skills, and receive education benefits, but it may involve more uncertainty regarding job assignments and deployments.
| Aspect | Military Academy | Enlisting |
|---|---|---|
| Education | Free 4-year college education | Tuition assistance and GI Bill benefits |
| Role | Officer | Enlisted |
| Commitment | Typically 5 years | 2-6 years |
| Lifestyle | More formal, leadership role | Varies by job and deployment |

Preparation and Application Process
For those interested in attending a military academy, preparation should begin early, ideally in high school. This includes maintaining a high GPA, performing well on the SAT or ACT, and engaging in extracurricular activities that demonstrate leadership and character. The application process involves nomination by a congressional representative, submitting an application package, and passing a medical exam and fitness test.To enlist, one must meet basic eligibility requirements, such as being a U.S. citizen, being between the ages of 17 and 35, and passing the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test. The process involves consulting with a recruiter, choosing a Military Occupational Specialty (MOS), and completing basic training.
In summary, the choice between attending a military academy and enlisting in the military depends on individual preferences, career goals, and personal circumstances. Both paths offer the opportunity to serve one’s country and can lead to rewarding careers, but they differ in terms of education, role, commitment, and lifestyle. By understanding these differences and considering one’s own strengths and aspirations, individuals can make an informed decision about which path is right for them.

What are the primary differences between attending a military academy and enlisting?
+The primary differences include the type of education received, the role within the military (officer vs. enlisted), the length of service commitment, and the lifestyle associated with each path.

How competitive is the process of getting accepted into a military academy?
+It is highly competitive, requiring a strong academic record, high scores on standardized tests, and nominations from congressional representatives. Only a small percentage of applicants are accepted each year.

What kind of education benefits are available to enlisted members?
+Enlisted members can receive tuition assistance for college courses taken while in service and are eligible for the GI Bill, which can be used for education expenses after leaving the military.



