Mechanical System In Use
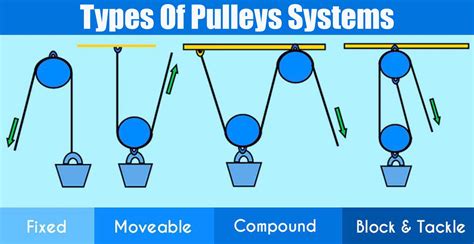
The mechanical system is an intricate network of components working together to ensure the smooth operation of various machines and structures. From simple mechanisms to complex industrial processes, understanding the mechanical system is crucial for anyone involved in engineering, manufacturing, or maintenance. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of mechanical systems, exploring their basic principles, common components, and real-world applications.
Understanding the Basics of Mechanical Systems

A mechanical system can be defined as an arrangement of interconnected parts that transmit and control force, motion, and energy. These systems are designed to perform specific tasks and achieve desired outcomes. Whether it's a simple lever or a sophisticated robotic arm, mechanical systems rely on the principles of mechanics and physics to function effectively.
At its core, a mechanical system consists of three main elements: inputs, outputs, and the mechanism itself. The input is the force or energy that initiates the system's operation, such as a person pushing a button or a motor starting a machine. The output is the result or action produced by the system, like the movement of a conveyor belt or the opening of a valve. The mechanism, often a combination of mechanical components, transforms the input into the desired output.
Mechanical systems can be classified into two main categories: simple machines and complex machines. Simple machines, such as levers, pulleys, and screws, are basic mechanical devices that provide mechanical advantage and amplify force. They are fundamental building blocks for more complex systems. Complex machines, on the other hand, are composed of multiple simple machines and other components, forming intricate assemblies to perform specific functions.
Key Components of Mechanical Systems
Mechanical systems are made up of various components, each serving a specific purpose. Here are some of the most common components found in mechanical systems:
- Bearing: Bearings are devices that allow smooth, low-friction movement between two parts. They are essential for reducing friction and wear, ensuring efficient motion.
- Gear: Gears are toothed wheels that transmit motion and force between rotating shafts. They can change the speed, direction, or torque of a system, allowing for precise control.
- Cam: Cams are mechanical components that translate rotational motion into linear motion. They are often used to control the timing and movement of other parts in a system.
- Piston: Pistons are cylindrical components that move within a cylinder, converting reciprocating motion into rotary motion or vice versa. They are commonly found in engines and pumps.
- Linkage: Linkages are mechanical connections that transmit motion and force between different parts. They can be used to create complex motion patterns and synchronize movements.
- Spring: Springs are elastic objects that store and release energy. They provide resistance, absorb shocks, and can be used for various purposes, such as in suspension systems or as a return mechanism.
These components, along with many others, work together to create intricate mechanical systems. The design and arrangement of these components determine the functionality and efficiency of the system.
Real-World Applications of Mechanical Systems

Mechanical systems are ubiquitous in our daily lives and across various industries. Here are some examples of how mechanical systems are utilized:
- Automotive Industry: Cars, trucks, and motorcycles rely on mechanical systems for their operation. From the engine and transmission to the suspension and braking systems, mechanical components ensure smooth and efficient transportation.
- Manufacturing and Industrial Processes: Mechanical systems are the backbone of many manufacturing processes. Conveyor belts, assembly lines, and robotic arms are all examples of mechanical systems that streamline production and increase efficiency.
- Construction and Engineering: Cranes, bulldozers, and excavators are heavy machinery that utilize mechanical systems to lift, move, and shape materials. These systems enable the construction of buildings, roads, and infrastructure.
- Aerospace: Aircraft, both commercial and military, incorporate advanced mechanical systems. From the propulsion systems to the flight control surfaces, mechanical components ensure safe and efficient air travel.
- Home Appliances: Everyday appliances like washing machines, refrigerators, and air conditioners rely on mechanical systems for their functionality. These systems ensure the proper operation and control of various processes.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Mechanical Systems

Regular maintenance is crucial for the optimal performance and longevity of mechanical systems. Here are some key maintenance practices:
- Inspection: Regularly inspect all components for wear, damage, or misalignment. Look for signs of corrosion, excessive wear, or loose connections.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential to reduce friction and prevent premature wear. Ensure that all moving parts are adequately lubricated according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Cleaning: Keep the system clean and free from debris. Dirt and contaminants can hinder performance and cause damage over time.
- Calibration: Calibrate sensors, gauges, and other measurement devices to ensure accurate readings. Calibration helps maintain the system's precision and reliability.
- Replacement: Replace worn-out or damaged components as needed. Regularly check critical parts and replace them before they fail, ensuring uninterrupted operation.
When troubleshooting mechanical systems, it's important to follow a systematic approach. Start by identifying the symptoms and isolating the problem. Check for common issues such as misalignment, binding, or faulty components. Refer to the system's manual or consult with experts to diagnose and resolve the issue effectively.
Future Trends in Mechanical Systems

The field of mechanical systems is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the need for increased efficiency and sustainability. Here are some future trends to watch out for:
- Smart Sensors and IoT: The integration of smart sensors and the Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming mechanical systems. These sensors can monitor and collect data in real-time, providing valuable insights for predictive maintenance and optimizing system performance.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing): Additive manufacturing is revolutionizing the production of mechanical components. It allows for the creation of complex geometries and customized parts, reducing lead times and costs.
- Robotics and Automation: Robotics and automation are becoming increasingly prevalent in mechanical systems. They enhance precision, speed, and efficiency, especially in repetitive tasks and hazardous environments.
- Sustainable and Green Technologies: There is a growing focus on developing mechanical systems that are environmentally friendly and energy-efficient. This includes the use of renewable energy sources, improved insulation, and the adoption of sustainable materials.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being applied to mechanical systems to optimize performance, predict failures, and enhance decision-making. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, improving system reliability and efficiency.
Conclusion

Mechanical systems are an integral part of our modern world, powering industries, transportation, and everyday appliances. Understanding the principles, components, and applications of mechanical systems is essential for anyone working in engineering, manufacturing, or maintenance. By staying up-to-date with the latest trends and best practices, we can continue to innovate and improve the efficiency and sustainability of mechanical systems.
What are some common issues with mechanical systems and how can they be prevented?
+
Common issues with mechanical systems include wear and tear, misalignment, and component failure. To prevent these issues, regular maintenance, proper lubrication, and timely component replacement are crucial. Additionally, implementing predictive maintenance strategies and using condition monitoring techniques can help identify potential problems before they cause system failure.
How can mechanical systems be optimized for energy efficiency?

+
Mechanical systems can be optimized for energy efficiency by reducing friction, improving aerodynamics, and using energy-efficient components. Regular maintenance, proper lubrication, and the adoption of energy-saving technologies can also contribute to increased energy efficiency. Additionally, implementing smart controls and optimizing system settings can further enhance energy savings.
What are the key considerations when designing a mechanical system?

+
When designing a mechanical system, several key considerations come into play. These include determining the system’s purpose and requirements, selecting appropriate components and materials, considering safety and regulatory standards, and optimizing the system for efficiency and reliability. It’s crucial to conduct thorough research, analyze potential risks, and involve experts in the design process to ensure a well-designed and functional mechanical system.

