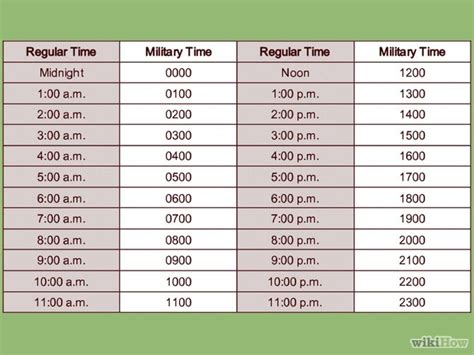
Independent Duty Medical Technician Role

Introduction to the Independent Duty Medical Technician Role
The Independent Duty Medical Technician (IDMT) role is a critical position in the military and other organizations that require medical care in remote or austere environments. IDMTs are trained to provide advanced medical care, often in situations where a physician is not available. They must be able to assess patients, diagnose conditions, and provide treatment, all while working independently with minimal supervision. In this blog post, we will explore the role of the IDMT, their responsibilities, and the skills and training required to be successful in this position.
Responsibilities of an Independent Duty Medical Technician
The responsibilities of an IDMT are diverse and demanding. Some of the key responsibilities include: * Providing advanced medical care, including diagnosing and treating illnesses and injuries * Conducting physical exams and taking medical histories * Ordering and interpreting laboratory tests and imaging studies * Developing and implementing treatment plans * Providing health education and counseling to patients * Maintaining accurate and detailed medical records * Collaborating with other healthcare professionals, such as physicians and nurses, to coordinate patient care IDMTs must be able to work independently, making decisions quickly and confidently, often in high-stress situations.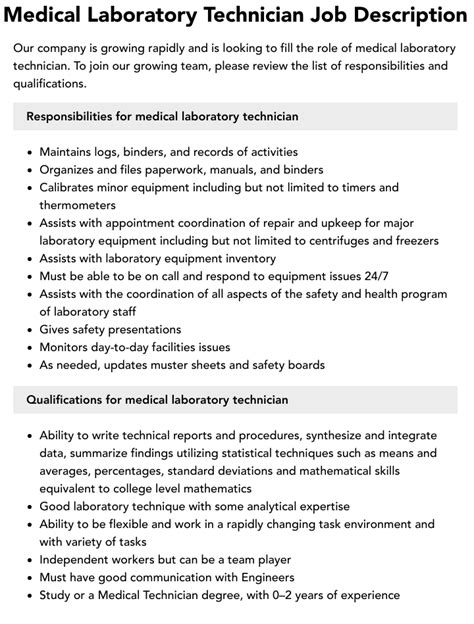
Skills and Training Required
To be successful as an IDMT, one must possess a unique combination of skills and training. Some of the key skills and training required include: * Advanced medical training, including certification as a medical technician or a similar professional certification * Strong assessment and diagnostic skills, including the ability to evaluate patients and diagnose conditions * Excellent communication and interpersonal skills, including the ability to communicate effectively with patients, families, and other healthcare professionals * Ability to work independently, with minimal supervision, in remote or austere environments * Strong problem-solving and critical thinking skills, including the ability to make quick and confident decisions in high-stress situations * Knowledge of medical protocols and procedures, including the ability to develop and implement treatment plans IDMTs must also be physically and mentally fit, able to work in a variety of environments, and willing to adapt to new and challenging situations.
Training and Certification
IDMTs typically require specialized training and certification. This training may include: * Completion of a medical technician training program * Certification as a medical technician or a similar professional certification * Completion of advanced training programs, such as the Independent Duty Medical Technician Course * Maintenance of certification through ongoing education and training The specific training and certification requirements may vary depending on the organization or employer.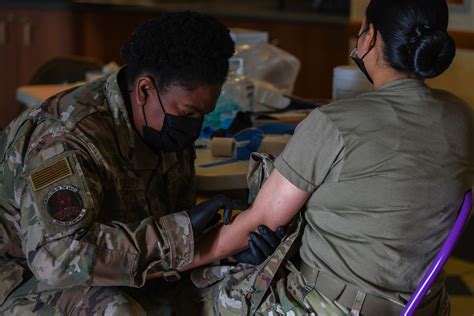
Work Environment
IDMTs may work in a variety of environments, including: * Military units, providing medical care to soldiers in remote or austere environments * Remote or rural areas, providing medical care to communities with limited access to healthcare * Disaster relief operations, providing medical care in response to natural disasters or other emergencies * Other organizations, such as non-governmental organizations (NGOs) or private companies, providing medical care in remote or austere environments IDMTs must be able to adapt to new and challenging environments, and be willing to work in a variety of settings.
Benefits and Challenges
The IDMT role offers many benefits, including: * Opportunities for advancement, including leadership positions and specialized training * Personal satisfaction, from providing medical care in challenging and rewarding environments * Variety and challenge, from working in a variety of environments and situations However, the IDMT role also presents many challenges, including: * High-stress work environment, with limited resources and support * Physical and mental demands, from working in remote or austere environments * Emotional toll, from working with patients in crisis situations IDMTs must be able to manage these challenges, while providing high-quality medical care to their patients.💡 Note: IDMTs must be able to work independently, with minimal supervision, in remote or austere environments. This requires strong assessment and diagnostic skills, excellent communication and interpersonal skills, and the ability to work well under pressure.

Conclusion and Future Outlook
In conclusion, the Independent Duty Medical Technician role is a critical position in the military and other organizations that require medical care in remote or austere environments. IDMTs must possess a unique combination of skills and training, including advanced medical training, strong assessment and diagnostic skills, and excellent communication and interpersonal skills. The IDMT role offers many benefits, including opportunities for advancement, personal satisfaction, and variety and challenge. However, it also presents many challenges, including high-stress work environments, physical and mental demands, and emotional toll. As the demand for medical care in remote or austere environments continues to grow, the role of the IDMT will become increasingly important.
What is the role of an Independent Duty Medical Technician?
+
The role of an Independent Duty Medical Technician is to provide advanced medical care in remote or austere environments, often with minimal supervision.

What skills and training are required to be an Independent Duty Medical Technician?
+
IDMTs require advanced medical training, strong assessment and diagnostic skills, excellent communication and interpersonal skills, and the ability to work independently with minimal supervision.

What are the benefits and challenges of being an Independent Duty Medical Technician?
+
The benefits of being an IDMT include opportunities for advancement, personal satisfaction, and variety and challenge. The challenges include high-stress work environments, physical and mental demands, and emotional toll.