Military
Inactive Duty Secrets


Understanding Inactive Duty: A Comprehensive Guide
Inactive duty refers to a status where a member of the military is not actively serving but is still part of the military reserves. This status can be confusing, especially for those who are new to the military or are considering joining. In this article, we will delve into the world of inactive duty, exploring its secrets, benefits, and what it means for those who serve.
Types of Inactive Duty
There are several types of inactive duty, each with its own set of rules and regulations. These include: * Ready Reserve: This is the most common type of inactive duty, where members are required to drill one weekend a month and attend annual training for two weeks. * Standby Reserve: Members in this category are not required to drill or attend annual training but can be called to active duty in times of war or national emergency. * Retired Reserve: This category is for members who have retired from the military but are still eligible to be called back to active duty.
Benefits of Inactive Duty
Inactive duty offers several benefits, including: * Education assistance: Members of the inactive reserve may be eligible for education assistance, such as the GI Bill, to help pay for college or vocational training. * Health insurance: Inactive reserve members may be eligible for health insurance through the military, which can be a significant cost savings. * Retirement benefits: Members who serve in the inactive reserve may be eligible for retirement benefits, including a pension and access to military bases and facilities.
Drawbacks of Inactive Duty
While inactive duty offers several benefits, there are also some drawbacks to consider: * Limited career advancement: Members of the inactive reserve may have limited opportunities for career advancement, as they are not actively serving. * Deployment risk: Inactive reserve members can be called to active duty in times of war or national emergency, which can be a significant risk. * Training requirements: Inactive reserve members are required to attend annual training and may be required to drill one weekend a month, which can be time-consuming and disrupt family and work plans.
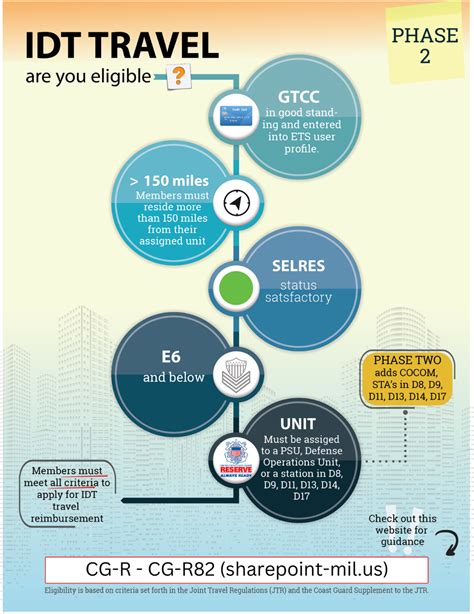
Eligibility Requirements
To be eligible for inactive duty, members must meet certain requirements, including: * Age: Members must be between the ages of 17 and 35 to join the inactive reserve. * Citizenship: Members must be U.S. citizens or resident aliens. * Education: Members must have a high school diploma or equivalent. * Physical fitness: Members must meet certain physical fitness standards to join the inactive reserve.📝 Note: These requirements may vary depending on the branch of the military and the specific job or role.

How to Join the Inactive Reserve
To join the inactive reserve, members must follow these steps: * Meet the eligibility requirements: Members must meet the age, citizenship, education, and physical fitness requirements. * Choose a branch: Members must choose which branch of the military they want to join, such as the Army, Navy, Air Force, or Marine Corps. * Enlist or commission: Members must enlist or receive a commission in the inactive reserve. * Complete basic training: Members must complete basic training, which can last several weeks or months.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, inactive duty is a complex and multifaceted topic that offers several benefits and drawbacks. Members who are considering joining the inactive reserve must carefully weigh the pros and cons and consider their individual circumstances and goals. By understanding the secrets of inactive duty, members can make informed decisions about their military careers and plan for their futures.
What is the difference between active duty and inactive duty?
+Active duty refers to full-time military service, while inactive duty refers to part-time military service in the reserves.
Can I join the inactive reserve if I have a felony conviction?
+It may be possible to join the inactive reserve with a felony conviction, but it will depend on the specific circumstances and the branch of the military.

How long do I have to serve in the inactive reserve?
+The length of service in the inactive reserve varies depending on the branch of the military and the specific job or role, but it is typically 6-8 years.


