Hughes Syndrome And Pregnancy

Hughes syndrome, also known as antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), is an autoimmune disorder that can have significant implications for women during pregnancy. This condition is characterized by the body's production of antiphospholipid antibodies, which can lead to various complications. Understanding Hughes syndrome and its impact on pregnancy is crucial for expectant mothers and healthcare professionals alike. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of Hughes syndrome, exploring its symptoms, diagnosis, and most importantly, its management during pregnancy to ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby.
Understanding Hughes Syndrome

Hughes syndrome is an autoimmune disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly produces antibodies against certain phospholipids and proteins in the blood. These antibodies can disrupt normal blood clotting processes, leading to a range of potential health issues.
Symptoms of Hughes Syndrome

- Blood clots in various parts of the body, such as the legs (deep vein thrombosis) or lungs (pulmonary embolism)
- Recurrent miscarriages or complications during pregnancy
- Skin changes, including livedo reticularis (a net-like pattern of blood vessels)
- Stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Headaches and migraine
- Memory loss and cognitive issues
It's important to note that not all individuals with Hughes syndrome will experience these symptoms, and the severity can vary widely.
Diagnosis of Hughes Syndrome

Diagnosing Hughes syndrome involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The following tests may be used:
- Antiphospholipid Antibody Tests: These tests detect the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies in the blood.
- Lupus Anticoagulant Test: This test helps identify the presence of lupus anticoagulant, another type of antiphospholipid antibody.
- Blood Clotting Tests: These tests assess the time it takes for blood to clot, providing insights into potential clotting disorders.
Diagnosis can be challenging, as symptoms may overlap with other conditions. A comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential.
Hughes Syndrome and Pregnancy

Hughes syndrome can significantly impact pregnancy, and it is crucial for women with this condition to receive specialized care and management during this time.
Complications During Pregnancy

- Miscarriage: Women with Hughes syndrome are at an increased risk of miscarriage, especially in the first trimester.
- Preterm Birth: The condition can lead to premature birth, often due to preeclampsia or other pregnancy-related complications.
- Preeclampsia: Hughes syndrome is associated with an elevated risk of preeclampsia, a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and organ damage.
- Fetal Growth Restriction: The baby's growth may be restricted, leading to a smaller-than-expected birth weight.
- Stillbirth: In rare cases, Hughes syndrome can contribute to stillbirth, although this is less common with proper management.
Managing Hughes Syndrome During Pregnancy

The goal of managing Hughes syndrome during pregnancy is to prevent complications and ensure a healthy outcome for both the mother and baby. Here are some key aspects of management:
- Anticoagulation Therapy: Low-dose aspirin and anticoagulant medications, such as heparin, are commonly prescribed to prevent blood clots and reduce the risk of pregnancy loss.
- Regular Monitoring: Close monitoring of the mother's health and the baby's growth is essential. This may include frequent ultrasound scans and blood tests.
- Fetal Surveillance: Specialized fetal surveillance techniques, such as Doppler ultrasound, may be used to assess the baby's well-being.
- Delivery Planning: Healthcare providers will work with the mother to develop a delivery plan, considering the timing and mode of delivery to minimize risks.
- Postpartum Care: After delivery, the mother may require continued anticoagulation therapy to prevent blood clots.
Living with Hughes Syndrome

Managing Hughes syndrome is a lifelong process, and individuals with this condition should work closely with their healthcare team to maintain their health. Here are some key considerations:
Lifestyle Modifications

- Maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine to promote overall well-being.
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these can increase the risk of blood clots.
- Manage stress levels through relaxation techniques and support groups.
Medication Management
Individuals with Hughes syndrome may require long-term medication to manage their condition. This may include anticoagulant medications and other medications to control symptoms.
Regular Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the condition and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Hughes Syndrome and Fertility
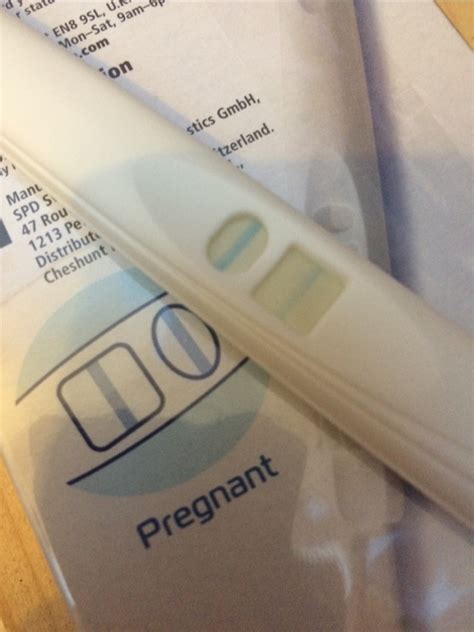
Hughes syndrome can also impact fertility. Women with this condition may experience difficulty conceiving due to the increased risk of blood clots and other complications. However, with proper management and medical assistance, many women with Hughes syndrome can successfully become pregnant and carry a healthy baby to term.
Support and Resources

Living with Hughes syndrome can be challenging, but support is available. Consider the following resources:
- Support groups and online communities can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Educational materials and websites, such as those provided by patient organizations, can offer valuable information about Hughes syndrome and its management.
- Consulting with a healthcare team that specializes in autoimmune disorders and pregnancy can be beneficial.
Conclusion

Hughes syndrome is a complex autoimmune disorder that requires careful management, especially during pregnancy. With early diagnosis, proper treatment, and a dedicated healthcare team, women with Hughes syndrome can have successful pregnancies and deliver healthy babies. It is essential for individuals with this condition to stay informed, maintain regular check-ups, and seek support when needed. By understanding and managing Hughes syndrome, we can work towards better outcomes for both mothers and their children.
Can Hughes syndrome be cured completely?

+
Hughes syndrome is a chronic condition, and there is currently no cure. However, with proper management and treatment, symptoms can be controlled, and the risk of complications can be significantly reduced.
What are the long-term effects of Hughes syndrome on a person’s health?

+
Long-term effects can vary, but Hughes syndrome can increase the risk of blood clots, stroke, and other cardiovascular issues. Regular monitoring and medication can help manage these risks effectively.
How does Hughes syndrome impact daily life and activities?

+
For many individuals, Hughes syndrome may not significantly impact daily life. However, it’s important to follow a healthy lifestyle and take prescribed medications as directed. In some cases, individuals may need to make adjustments to their activities to manage their condition effectively.

