Green Beret Physical Standards


Introduction to Green Beret Physical Standards
The Green Berets, also known as the United States Army Special Forces, are an elite group of soldiers who undergo rigorous training to become experts in unconventional warfare, foreign language, and cultural expertise. To become a Green Beret, one must meet specific physical standards that test their endurance, strength, and agility. These physical standards are designed to ensure that soldiers can perform their duties effectively in challenging environments.
Physical Requirements for Green Beret Training
To be eligible for Green Beret training, soldiers must meet the following physical requirements:- Age: Between 20 and 35 years old (with some exceptions for older candidates)
- Weight: Meet the Army’s weight standards for their height
- Body Fat Percentage: Less than 24% for men and less than 36% for women
- Push-ups: Perform a minimum of 30 push-ups in 1 minute
- Sit-ups: Perform a minimum of 30 sit-ups in 1 minute
- 2-mile Run: Complete a 2-mile run in less than 14 minutes for men and less than 15 minutes for women
- Swimming: Pass a swim test, which includes swimming 100 meters using any stroke
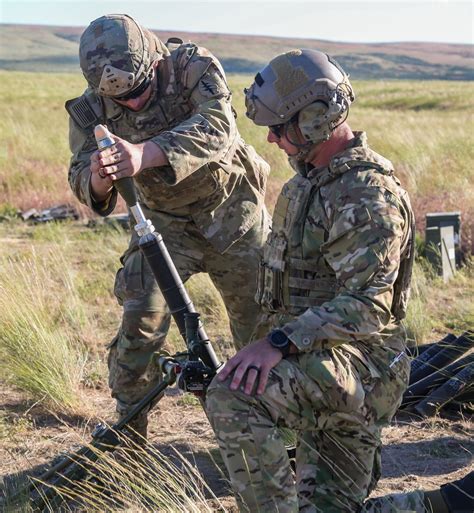

Special Forces Assessment and Selection (SFAS)
After meeting the initial physical requirements, soldiers who want to become Green Berets must attend the Special Forces Assessment and Selection (SFAS) course. This 24-day course is designed to evaluate a soldier’s physical and mental abilities, as well as their leadership and teamwork skills. The SFAS course includes a variety of physical challenges, such as:- Ruck marches: Carrying a heavy backpack over long distances
- Obstacle courses: Completing obstacle courses that test agility and endurance
- Swimming and water survival: Passing a swim test and demonstrating water survival skills
- Land navigation: Using a map and compass to navigate through challenging terrain

Green Beret Training Pipeline
After completing SFAS, soldiers who are selected to become Green Berets will attend the Special Forces Qualification Course (SFQC), also known as the “Q Course.” This course is approximately 62 weeks long and includes advanced training in:- Language skills: Learning a foreign language, such as Spanish, French, or Arabic
- Cultural expertise: Studying the culture and customs of a specific region
- Unconventional warfare: Learning tactics and techniques for unconventional warfare, such as guerrilla warfare and sabotage
- Advanced first aid: Learning advanced first aid and medical skills
💪 Note: The Green Beret training pipeline is extremely challenging, both physically and mentally. Soldiers who are selected to become Green Berets must be in top physical condition and have a strong mental toughness to succeed.

Physical Standards for Green Beret Missions
Green Berets are often deployed to challenging environments, such as remote or mountainous areas, where they must be able to perform their duties effectively. The physical standards for Green Beret missions include:- Carrying heavy loads: Carrying heavy backpacks or equipment over long distances
- Operating in extreme weather: Operating in extreme temperatures, such as hot or cold weather
- Using specialized equipment: Using specialized equipment, such as parachutes or scuba gear
- Conducting long-range patrols: Conducting long-range patrols, which can last for several days or weeks

| Event | Minimum Standard |
|---|---|
| 2-mile Run | Less than 14 minutes for men, less than 15 minutes for women |
| Push-ups | 30 push-ups in 1 minute |
| Sit-ups | 30 sit-ups in 1 minute |
| Swimming | Pass a swim test, which includes swimming 100 meters using any stroke |

Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In summary, the physical standards for becoming a Green Beret are extremely challenging and require a high level of physical fitness, endurance, and agility. Soldiers who want to become Green Berets must meet specific physical requirements, complete the SFAS course, and attend the SFQC to learn advanced skills in language, culture, and unconventional warfare. The physical standards for Green Beret missions are also demanding, requiring soldiers to carry heavy loads, operate in extreme weather, and conduct long-range patrols. By understanding the physical standards for becoming a Green Beret, soldiers can prepare themselves for the challenges of this elite group and serve their country with honor and distinction.
What are the physical requirements for Green Beret training?
+The physical requirements for Green Beret training include meeting the Army’s weight standards, having a body fat percentage of less than 24% for men and less than 36% for women, performing a minimum of 30 push-ups and 30 sit-ups in 1 minute, completing a 2-mile run in less than 14 minutes for men and less than 15 minutes for women, and passing a swim test.

What is the Special Forces Assessment and Selection (SFAS) course?
+The SFAS course is a 24-day course that evaluates a soldier’s physical and mental abilities, as well as their leadership and teamwork skills. The course includes a variety of physical challenges, such as ruck marches, obstacle courses, swimming and water survival, and land navigation.

What is the Green Beret training pipeline?
+The Green Beret training pipeline includes the SFAS course, followed by the Special Forces Qualification Course (SFQC), also known as the “Q Course.” The Q Course is approximately 62 weeks long and includes advanced training in language skills, cultural expertise, unconventional warfare, and advanced first aid.