Erikson Stages Of Development Chart
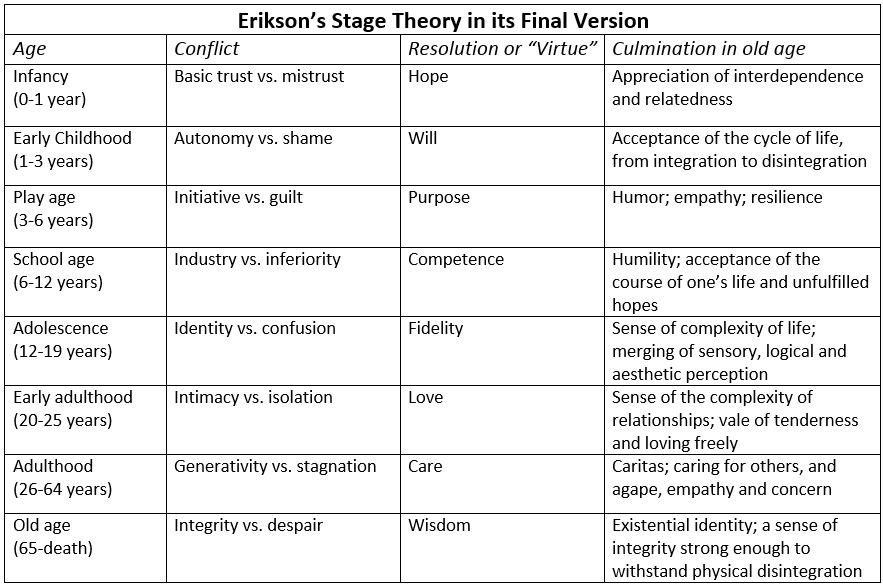
The Erikson Stages of Development chart is a visual representation of the renowned psychologist Erik Erikson's theory on psychosocial development. This theory proposes that human development is a series of stages, each characterized by a specific conflict or challenge that must be resolved to progress to the next stage.
Erikson's theory is widely recognized and has had a significant impact on our understanding of human growth and personality formation. It provides a comprehensive framework for exploring the various aspects of our lives, from infancy to old age. Let's delve into the details of each stage and uncover the key insights and challenges associated with them.
The Eight Stages of Psychosocial Development

Erikson's theory consists of eight distinct stages, each with its own unique crisis or conflict. These stages are as follows:
-
Trust vs. Mistrust (Infancy: 0-18 months)
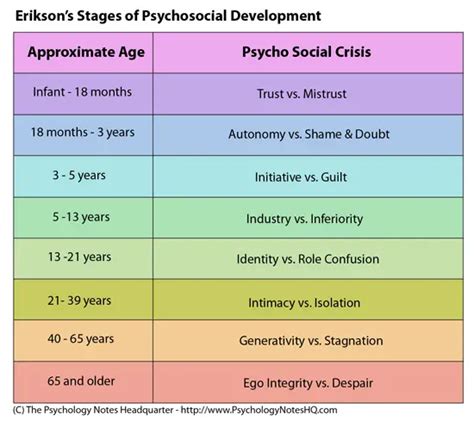
In the first stage, infants must develop a sense of trust in their caregivers. A secure and nurturing environment fosters trust, while neglect or abuse can lead to feelings of mistrust and anxiety.
-
Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt (Early Childhood: 18 months - 3 years)

As toddlers gain more control over their bodies, they strive for independence. Success in this stage leads to a sense of autonomy, while excessive control or criticism may result in shame and self-doubt.
-
Initiative vs. Guilt (Preschool: 3-6 years)

Preschoolers begin to assert their will and take initiative. Encouraging this behavior promotes a sense of initiative, while excessive restrictions or punishments may lead to feelings of guilt.
-
Industry vs. Inferiority (School Age: 6-12 years)

During this stage, children face the challenge of mastering new skills and knowledge. Success leads to a sense of competence and industry, while failure may result in feelings of inferiority.
-
Identity vs. Role Confusion (Adolescence: 12-18 years)

Adolescents struggle to establish their unique identity and sense of self. A successful resolution results in a strong sense of identity, while confusion or uncertainty may lead to role confusion.
-
Intimacy vs. Isolation (Young Adulthood: 18-40 years)

Young adults seek close relationships and intimacy. Forming meaningful connections fosters intimacy, while difficulties in relationships may lead to feelings of isolation.
-
Generativity vs. Stagnation (Middle Adulthood: 40-65 years)

In middle adulthood, individuals focus on contributing to society and nurturing the next generation. Engaging in meaningful work and relationships promotes generativity, while a lack of purpose may lead to stagnation.
-
Ego Integrity vs. Despair (Late Adulthood: 65+ years)
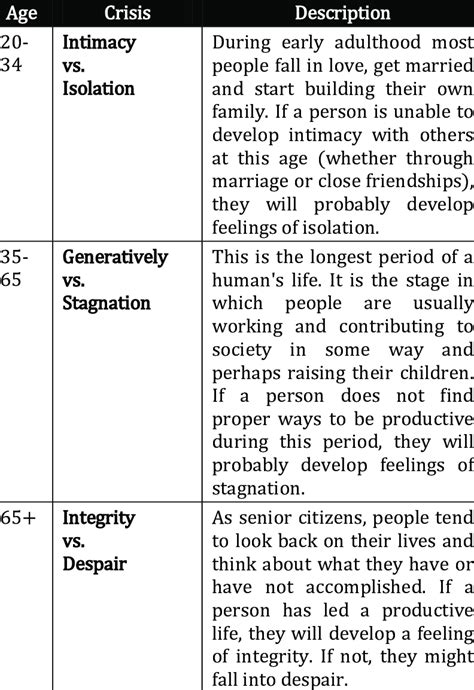
As individuals enter late adulthood, they reflect on their lives and strive for a sense of integrity. Accepting one's life and its accomplishments brings integrity, while regret and dissatisfaction may lead to despair.
The Erikson Stages of Development Chart

Here's a simplified chart illustrating the eight stages of Erikson's theory:
| Stage | Age | Conflict | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trust vs. Mistrust | 0-18 months | Trust in caregivers | Hope |
| Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt | 18 months - 3 years | Independence | Willpower |
| Initiative vs. Guilt | 3-6 years | Taking initiative | Purpose |
| Industry vs. Inferiority | 6-12 years | Mastering skills | Competence |
| Identity vs. Role Confusion | 12-18 years | Establishing identity | Fidelity |
| Intimacy vs. Isolation | 18-40 years | Close relationships | Love |
| Generativity vs. Stagnation | 40-65 years | Contributing to society | Care |
| Ego Integrity vs. Despair | 65+ years | Reflecting on life | Wisdom |

Key Takeaways

- Erikson's theory emphasizes the importance of resolving conflicts at each stage to ensure healthy development.
- The outcomes of each stage lay the foundation for the next, highlighting the interconnectedness of our psychological growth.
- Understanding these stages can provide valuable insights into our own development and that of our loved ones.
Final Thoughts

Erikson's Stages of Development chart offers a comprehensive roadmap for understanding human growth and development. By recognizing the challenges and conflicts associated with each stage, we can strive for a more fulfilling and balanced life. Remember, each stage builds upon the previous one, so it's essential to address any unresolved issues to ensure a healthy and happy journey through life.
🌟 Note: This blog post provides a concise overview of Erikson's theory. For a more in-depth exploration, consider reading Erik Erikson's original works or consulting academic resources on psychosocial development.
What is the significance of Erikson’s theory in psychology?

+
Erikson’s theory has greatly influenced our understanding of human development, providing a comprehensive framework for exploring the various aspects of our lives.
How can I apply Erikson’s theory in my personal life?

+
By understanding the challenges and outcomes of each stage, you can reflect on your own development and work towards resolving any unresolved conflicts.
Are there any criticisms of Erikson’s theory?
+Some critics argue that Erikson’s theory is too rigid and may not fully account for individual differences and cultural variations.
