Detroit Edison Monroe Power Plant

The Detroit Edison Monroe Power Plant, a formidable presence in the energy landscape of Michigan, stands as a testament to the state's commitment to powering its future. This coal-fired powerhouse, located in Monroe County, has been a cornerstone of the region's energy infrastructure for decades. In this blog post, we delve into the intricacies of this plant, exploring its history, operations, and the impact it has on the local community and environment.
A Brief History

The Detroit Edison Monroe Power Plant has a rich history that dates back to the early 20th century. It was initially conceived as a solution to the growing energy demands of the rapidly industrializing region. Construction began in the 1960s, and the plant became operational in the early 1970s. Over the years, it has undergone significant expansions and upgrades to keep pace with the evolving energy needs of Michigan.
The plant's early years were marked by innovation and a commitment to environmental stewardship. Detroit Edison, the company behind the plant, implemented cutting-edge technologies to minimize its environmental impact. This included the installation of advanced pollution control systems, which were ahead of their time in the industry.
Plant Operations and Technology

The Detroit Edison Monroe Power Plant is a coal-fired facility, utilizing this abundant and cost-effective fuel source to generate electricity. The plant's design and technology have evolved over the years, incorporating state-of-the-art equipment to enhance efficiency and reduce emissions.
Coal Handling and Storage

Coal is delivered to the plant via a dedicated rail system, ensuring a steady supply of fuel. Upon arrival, the coal undergoes a rigorous process of crushing and grinding to achieve the desired size for combustion. This finely ground coal is then stored in massive silos, ready for use in the boilers.
Boiler Technology
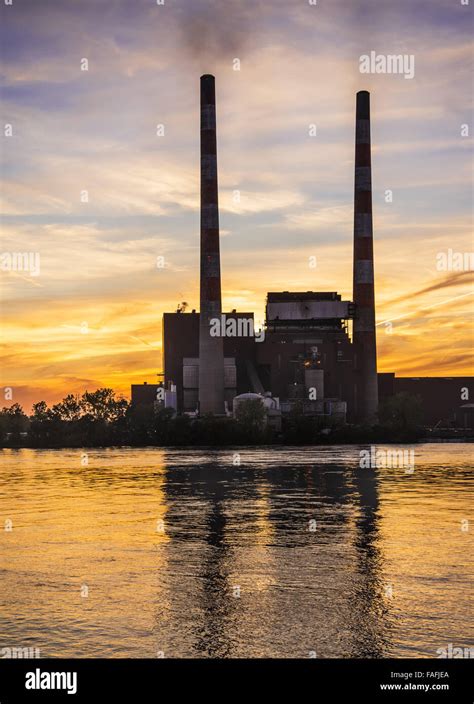

The heart of the Detroit Edison Monroe Power Plant lies in its boilers. These massive structures are designed to burn coal efficiently, generating high-pressure steam. The plant utilizes supercritical boilers, which operate at extremely high temperatures and pressures, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced emissions.
Steam Turbines and Generators

The high-pressure steam produced by the boilers is directed towards the steam turbines. These turbines, driven by the force of the steam, rotate at high speeds. This rotational energy is then converted into electrical energy by the generators, which are directly coupled to the turbines. The generators produce electricity, which is fed into the grid to power homes and businesses across Michigan.
Emission Control Systems

One of the key strengths of the Detroit Edison Monroe Power Plant is its commitment to environmental responsibility. The plant is equipped with advanced emission control systems, including scrubbers and filters, to minimize the release of pollutants into the atmosphere. These systems help reduce sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, ensuring compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
Impact on the Community and Environment

The Detroit Edison Monroe Power Plant has had a significant impact on the local community and the environment. Here's a closer look at these effects:
Economic Benefits

- Job Creation: The plant provides employment opportunities for hundreds of skilled workers, contributing to the local economy.
- Tax Revenue: As a major industrial facility, the plant generates substantial tax revenue for the county and state, supporting public services and infrastructure.
- Stimulus for Local Businesses: The presence of the power plant stimulates local businesses, from supply chain partners to restaurants and retail stores.
Environmental Considerations

- Emission Reduction: The plant's commitment to emission control has led to a significant reduction in air pollutants, benefiting the health and well-being of the community.
- Water Usage: The plant's water intake and discharge systems are carefully managed to minimize the impact on local water resources.
- Land Use: The plant's footprint has been optimized to minimize the disruption of natural habitats and ecosystems.
Community Engagement

Detroit Edison, the plant's operator, actively engages with the local community. This includes hosting educational programs, supporting local initiatives, and providing scholarships for students pursuing STEM careers. The company's commitment to community outreach fosters a positive relationship with the residents of Monroe County.
Future Prospects and Sustainability

As the energy landscape evolves, the Detroit Edison Monroe Power Plant is adapting to meet the changing needs of Michigan. The plant is exploring the integration of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, to diversify its energy portfolio. Additionally, the company is investing in research and development to further enhance its environmental performance and reduce its carbon footprint.
In conclusion, the Detroit Edison Monroe Power Plant is a vital component of Michigan's energy infrastructure. Its rich history, advanced technology, and commitment to environmental stewardship make it a key player in the state's energy future. As the plant continues to evolve, it will play a crucial role in powering the region while minimizing its impact on the environment and contributing to the well-being of the local community.
What is the capacity of the Detroit Edison Monroe Power Plant?

+
The Detroit Edison Monroe Power Plant has a total capacity of approximately 1,800 megawatts, making it one of the largest coal-fired power plants in the United States.
How does the plant ensure environmental compliance?

+
The plant employs a comprehensive environmental management system, including regular monitoring and reporting, to ensure compliance with federal, state, and local regulations. This includes emissions monitoring, water quality testing, and waste management practices.
What are the future plans for the plant’s expansion or transition to renewable energy?

+
Detroit Edison is actively exploring options for integrating renewable energy sources into the plant’s operations. This includes the potential addition of solar and wind power generation facilities, as well as the development of energy storage solutions to support the transition to a more sustainable energy future.