Design The Ultimate Portal To Portal Act Strategy Now
Creating an effective strategy for the Portal to Portal Act is crucial for businesses to ensure compliance and navigate the complexities of wage and hour laws. This blog post will guide you through the process of designing an ultimate strategy, covering various aspects and providing valuable insights.
Understanding the Portal to Portal Act

The Portal to Portal Act, also known as the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), is a federal law in the United States that governs wage and hour regulations. It aims to protect employees' rights by establishing minimum wage, overtime pay, and recordkeeping requirements. Understanding the key provisions of this act is essential for employers to avoid legal complications.
Key Provisions of the Portal to Portal Act
- Minimum Wage: The act sets a minimum hourly wage rate that employers must pay their employees. Currently, the federal minimum wage is $7.25 per hour, but some states and cities have higher minimum wage laws.
- Overtime Pay: Employees who work more than 40 hours in a workweek are entitled to overtime pay, which is typically time and a half their regular rate of pay. The Portal to Portal Act defines the rules for calculating and paying overtime.
- Recordkeeping: Employers are required to maintain accurate records of employees' hours worked, wages earned, and other relevant information. These records are crucial for compliance and can be used to resolve disputes or audits.
- Exemptions and Non-Exemptions: The act distinguishes between exempt and non-exempt employees. Exempt employees are typically executives, professionals, and administrative workers who are not entitled to overtime pay. Non-exempt employees, on the other hand, are covered by the overtime provisions.
Designing Your Portal to Portal Act Strategy

Developing a comprehensive strategy for complying with the Portal to Portal Act involves several key steps. By following these steps, you can ensure that your business remains compliant and avoids potential legal issues.
Step 1: Assess Your Workforce
The first step in designing your strategy is to assess your workforce. Identify the different categories of employees within your organization, such as exempt and non-exempt workers, and understand their roles and responsibilities. This assessment will help you determine the potential impact of the Portal to Portal Act on your business.
Step 2: Classify Employees
Classifying your employees correctly is crucial. Ensure that you understand the criteria for exempt and non-exempt employees. Exempt employees are typically those who exercise significant managerial or professional responsibilities and have a certain level of autonomy. Non-exempt employees, on the other hand, are entitled to overtime pay and are subject to stricter recordkeeping requirements.
Step 3: Implement Time Tracking Systems

To comply with the Portal to Portal Act, accurate time tracking is essential. Implement robust time tracking systems that allow you to record and monitor employees' hours worked. This can be done through traditional time cards or modern digital solutions like time tracking apps or software. Ensure that the system is user-friendly and accessible to both employees and management.
Step 4: Establish Overtime Policies
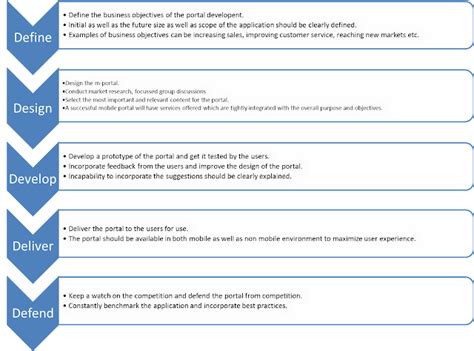
Develop clear and concise overtime policies that align with the Portal to Portal Act. Define the circumstances under which overtime work is permitted and the procedures for requesting and approving overtime. Communicate these policies to your employees and ensure that they understand their rights and responsibilities regarding overtime pay.
Step 5: Train and Educate Employees

Provide comprehensive training and education to your employees regarding the Portal to Portal Act. Explain the importance of accurate time tracking, the distinction between exempt and non-exempt employees, and the consequences of non-compliance. By empowering your employees with knowledge, you can foster a culture of compliance within your organization.
Step 6: Maintain Accurate Records
The Portal to Portal Act requires employers to maintain detailed records of employees' hours worked, wages earned, and other relevant information. Develop a robust recordkeeping system that ensures the accuracy and accessibility of these records. Regularly review and update your records to stay compliant and be prepared for any audits or investigations.
Step 7: Stay Updated on Legal Changes

Labor laws and regulations are subject to change, so it is crucial to stay updated on any amendments or modifications to the Portal to Portal Act. Subscribe to reliable sources of legal information, attend webinars or seminars, and consult with employment law experts to ensure that your strategy remains current and compliant.
Benefits of a Well-Designed Strategy

Implementing an effective Portal to Portal Act strategy offers several benefits to your business:
- Compliance: By following a well-designed strategy, you can ensure that your business remains compliant with the Portal to Portal Act, minimizing the risk of legal penalties and lawsuits.
- Cost Savings: Proper time tracking and overtime management can help you control labor costs and avoid unnecessary expenses associated with non-compliance.
- Improved Employee Morale: Transparent and fair compensation practices, as mandated by the Portal to Portal Act, can boost employee morale and satisfaction, leading to increased productivity.
- Enhanced Reputation: A commitment to compliance demonstrates your business's integrity and ethical practices, which can enhance your reputation among employees, clients, and stakeholders.
Conclusion

Designing an ultimate strategy for the Portal to Portal Act is essential for businesses to navigate the complexities of wage and hour laws. By assessing your workforce, classifying employees correctly, implementing effective time tracking systems, and staying updated on legal changes, you can ensure compliance and protect your business from potential legal issues. Remember, a well-designed strategy not only helps you avoid penalties but also fosters a positive work environment and boosts your reputation.
What is the Portal to Portal Act?
+
The Portal to Portal Act, also known as the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), is a federal law in the United States that governs wage and hour regulations, including minimum wage, overtime pay, and recordkeeping requirements.
Who is covered by the Portal to Portal Act?

+
The Portal to Portal Act applies to most employees in the United States, including both exempt and non-exempt workers. However, certain categories of employees, such as independent contractors, may not be covered by the act.
What are the key provisions of the Portal to Portal Act?
+The key provisions of the Portal to Portal Act include setting a minimum wage, requiring overtime pay for non-exempt employees working more than 40 hours in a workweek, and mandating recordkeeping practices for employers.
How can I ensure compliance with the Portal to Portal Act?
+To ensure compliance, businesses should assess their workforce, classify employees correctly, implement accurate time tracking systems, establish clear overtime policies, train employees on their rights and responsibilities, and maintain comprehensive records.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with the Portal to Portal Act?
+Non-compliance with the Portal to Portal Act can result in legal penalties, including fines and back wages owed to employees. It can also lead to negative publicity, damage to reputation, and potential lawsuits.



