A S O Titer
An ASO titer is a blood test that measures the level of antibodies produced by your immune system in response to a bacterial infection caused by Streptococcus bacteria, often referred to as strep. These antibodies, known as antistreptolysin O (ASO) antibodies, are specific to a toxin produced by certain strains of Streptococcus bacteria.
The ASO titer test is primarily used to diagnose and monitor infections caused by group A Streptococcus, which is a common cause of throat infections (strep throat) and certain skin infections. It helps healthcare professionals determine if a current or recent infection is due to this particular type of bacteria.
Understanding the ASO Titer Test
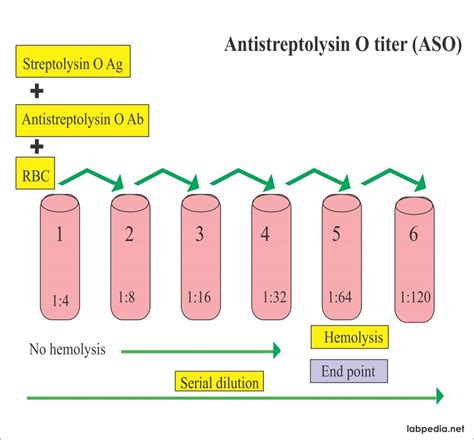
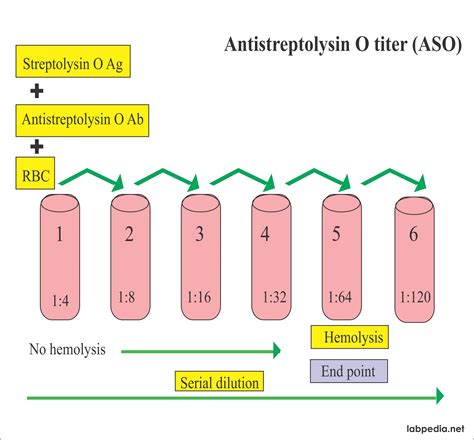
The ASO titer test is a laboratory procedure that measures the concentration of ASO antibodies in a person's blood. These antibodies are produced by the immune system as a response to the presence of Streptococcus bacteria. The test works by detecting and quantifying the level of these antibodies, which can indicate the severity and duration of the infection.
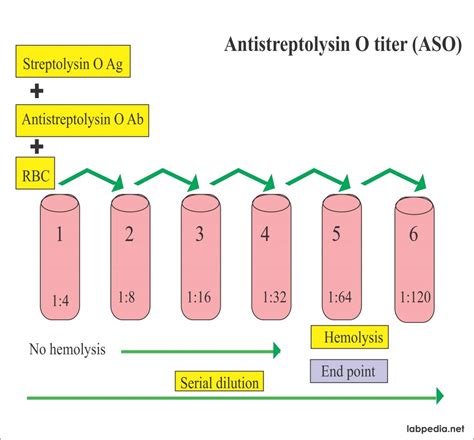
Here's a simplified breakdown of the ASO titer test process:
- Sample Collection: A healthcare professional will draw a blood sample from a vein in your arm. This sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- Laboratory Analysis: In the laboratory, the blood sample is tested for the presence and concentration of ASO antibodies. This is typically done using a technique called an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or a latex agglutination test.
- Result Interpretation: The results of the test are usually reported as a titer, which is a measure of the dilution of the blood sample at which the ASO antibodies can still be detected. A higher titer indicates a stronger immune response and potentially a more severe or recent infection.
When is an ASO Titer Test Ordered?
An ASO titer test is typically ordered when a healthcare provider suspects that a person has an infection caused by group A Streptococcus. Some common indications for ordering this test include:
- Persistent or recurrent sore throat, especially if it is accompanied by fever and swollen lymph nodes.
- Skin infections, such as impetigo or cellulitis, that are caused by Streptococcus bacteria.
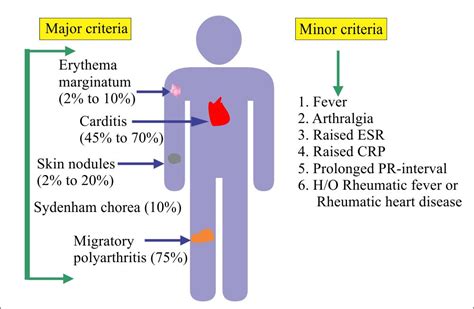
- Suspected cases of rheumatic fever, which is a rare but serious complication of untreated strep throat.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of antibiotic treatment for strep throat or skin infections.
Interpreting ASO Titer Results
The interpretation of ASO titer results can be complex and should be done by a healthcare professional. Generally, the following guidelines are used:
- Normal ASO Titer: A normal or negative ASO titer indicates that there are no detectable levels of ASO antibodies in the blood. This typically suggests that there is no recent or active infection with group A Streptococcus.
- Elevated ASO Titer: An elevated ASO titer suggests that the body is producing a significant amount of ASO antibodies in response to a recent or ongoing infection. The higher the titer, the more likely it is that the infection is recent or severe.
- Titer Trends: In some cases, healthcare providers may order multiple ASO titer tests over time to monitor the trend of antibody levels. A rising titer can indicate an active or recent infection, while a declining titer suggests that the infection is resolving.
Limitations and Considerations
While the ASO titer test is a valuable tool for diagnosing and monitoring group A Streptococcus infections, it does have some limitations:
- False Positives and Negatives: ASO titers can sometimes be elevated due to other infections or non-infectious conditions, leading to false positive results. Conversely, a negative ASO titer does not rule out a recent or ongoing infection, especially if the infection is in its early stages.
- Time Frame: It typically takes about 1-3 weeks after an infection for ASO antibodies to reach detectable levels. Therefore, an ASO titer test may not be useful in the immediate aftermath of an infection.
- Antibiotic Use: Antibiotic treatment for a Streptococcus infection can lower ASO titers, making it difficult to determine the effectiveness of treatment based on titer levels alone.
Preparing for the ASO Titer Test

No special preparation is usually required for an ASO titer test. However, it's always a good idea to inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking, as some drugs might affect the test results.
Procedure
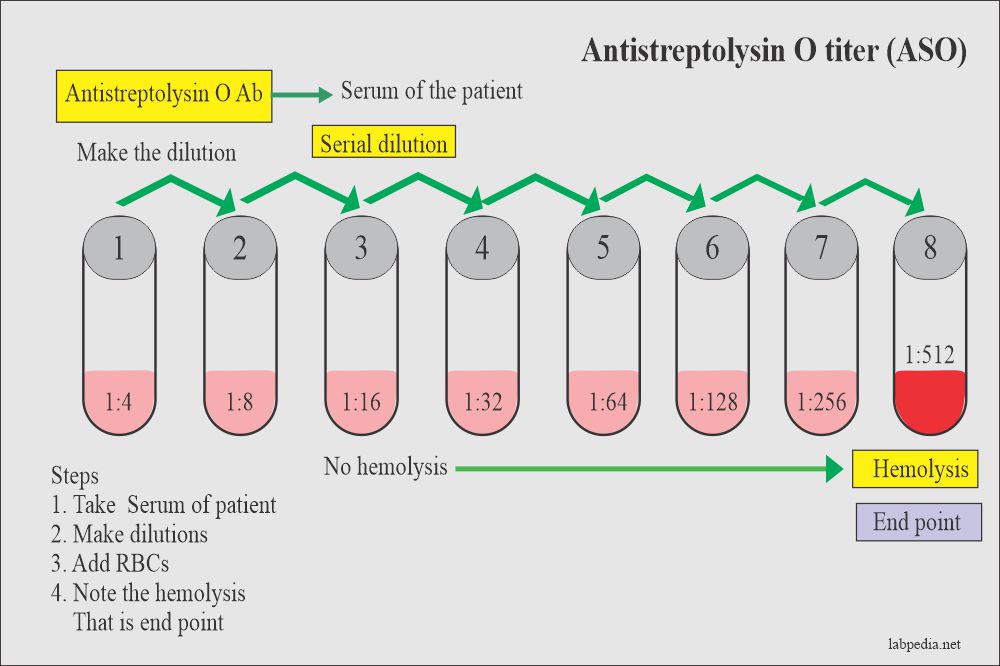
The ASO titer test is a simple blood test that involves the following steps:
- Sample Collection: A healthcare professional will use a needle to draw blood from a vein in your arm. This process is quick and typically not painful.
- Sample Handling: The blood sample is collected in a tube and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
- Laboratory Analysis: In the laboratory, the blood sample is tested using specialized techniques to measure the level of ASO antibodies.
Risks and Complications
The ASO titer test is a safe procedure with minimal risks. The most common risk is temporary discomfort or bruising at the site where the blood was drawn. In rare cases, individuals may experience lightheadedness or infection at the puncture site, but these complications are extremely rare.
Results and Follow-Up

ASO titer test results are typically available within a few days to a week. Your healthcare provider will discuss the results with you and determine the next steps, which may include further testing, treatment, or monitoring.
Treatment and Management
If the ASO titer test confirms a group A Streptococcus infection, your healthcare provider will likely prescribe a course of antibiotics to treat the infection. It's important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if you start feeling better before the medication is finished.
In some cases, especially if the infection is severe or has led to complications like rheumatic fever, additional treatments or monitoring may be necessary. Your healthcare provider will guide you through the appropriate management plan based on your specific situation.
Frequently Asked Questions

What is the purpose of the ASO titer test?
+
The ASO titer test is used to detect and quantify antibodies produced by the immune system in response to an infection caused by group A Streptococcus bacteria.
When is an ASO titer test typically ordered?

+
An ASO titer test is commonly ordered when a healthcare provider suspects a group A Streptococcus infection, especially in cases of persistent sore throat, skin infections, or suspected rheumatic fever.
How is the ASO titer test performed?

+
The test involves drawing a blood sample from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis to measure the level of ASO antibodies.
What do the results of an ASO titer test mean?
+
Elevated ASO titers suggest a recent or ongoing group A Streptococcus infection, while normal or negative titers indicate no recent or active infection.
Are there any risks associated with the ASO titer test?

+
The ASO titer test is a safe procedure with minimal risks. The most common risk is temporary discomfort or bruising at the blood draw site.
In conclusion, the ASO titer test is a valuable diagnostic tool for detecting and managing group A Streptococcus infections. While it has its limitations, it provides valuable information to healthcare providers, aiding in the timely diagnosis and treatment of these infections. Remember, if you suspect you have a strep infection, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.



