15 Ana Titer Facts: The Essential Guide To Understanding Results

Understanding Ana Titer Results: A Comprehensive Guide

Ana titer tests are an essential tool in medical diagnostics, providing valuable insights into a patient’s health. These tests measure the concentration of antibodies in the blood, offering crucial information about past infections, vaccinations, and immune system responses. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore 15 key facts about ana titer results, helping you understand their significance and implications.
1. What is an Ana Titer Test?
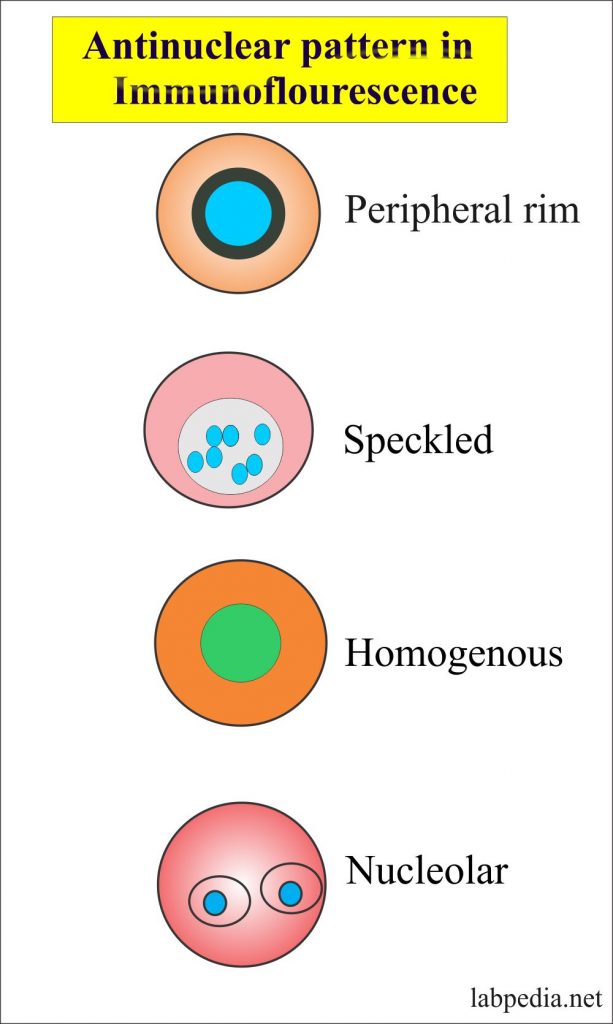
An ana titer test, also known as a serum antibody titer test, is a laboratory procedure used to measure the quantity or concentration of specific antibodies in an individual’s blood. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system in response to the presence of foreign substances, such as viruses, bacteria, or other antigens. The test helps assess an individual’s immune response and can provide valuable information about their health status.
2. How is an Ana Titer Test Performed?

The ana titer test involves taking a blood sample from the patient. The sample is then sent to a laboratory where it undergoes a series of steps to measure the antibody levels. The process typically includes:
- Blood Collection: A healthcare professional will draw a small amount of blood from a vein in the patient’s arm using a needle.
- Sample Preparation: The collected blood is allowed to clot, and the serum (the liquid portion of the blood) is separated from the cellular components.
- Serum Analysis: The serum is then diluted and mixed with specific antigens to trigger an immune response. The reaction between the antibodies and antigens is measured, providing the titer value.
3. Interpreting Ana Titer Results

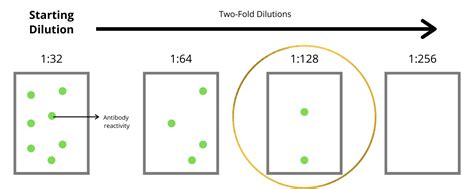
Interpreting ana titer results requires expertise and knowledge of the specific antibody being tested. The results are typically reported as a ratio or a dilution factor, indicating the strength of the immune response. A higher titer value suggests a stronger immune response and a higher concentration of antibodies.
4. Positive and Negative Results

- Positive Result: A positive ana titer result indicates the presence of antibodies against a specific antigen. It suggests that the individual has been exposed to the antigen, either through infection or vaccination.
- Negative Result: A negative result means that no antibodies were detected, indicating a lack of exposure to the antigen or a very low immune response.
5. Titer Values and Interpretation
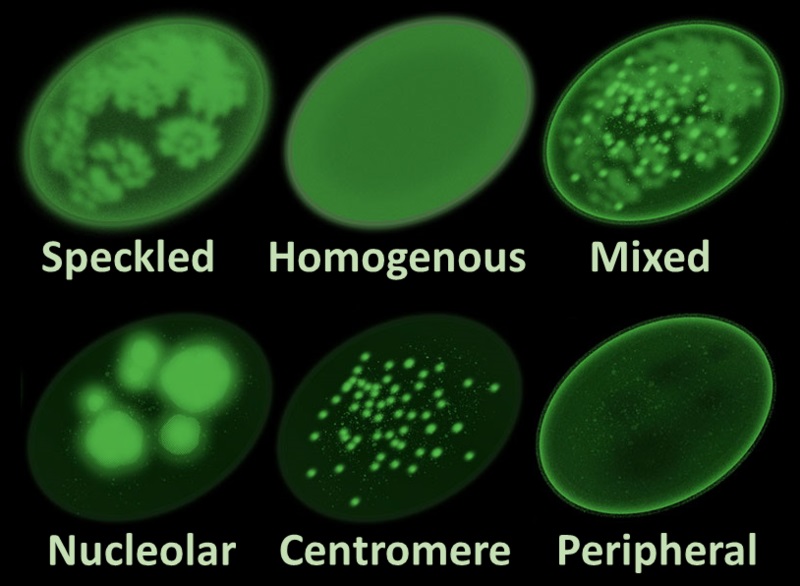
The titer value provides information about the concentration of antibodies. Here’s a simplified interpretation:
- High Titer Value: A high titer value suggests a strong immune response and a higher likelihood of protection against the specific antigen.
- Low Titer Value: A low titer value indicates a weaker immune response, which may require further evaluation or vaccination.
6. Different Types of Ana Titer Tests

There are various types of ana titer tests, each targeting specific antibodies. Some common types include:
- Rubella Titer Test: Measures antibodies against the rubella virus, often used to assess immunity in pregnant women.
- Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV) Titer Test: Detects antibodies to the virus that causes chickenpox and shingles.
- Measles Titer Test: Evaluates immunity to measles by measuring specific antibodies.
- Hepatitis B Titer Test: Assesses immunity to hepatitis B by detecting antibodies produced after vaccination or infection.
7. Importance of Ana Titer Tests

Ana titer tests play a crucial role in medical practice for several reasons:
- Vaccination Assessment: They help determine an individual’s immunity after vaccination, ensuring effective protection.
- Infection Diagnosis: Titer tests can aid in diagnosing past or current infections, especially in cases where symptoms are vague.
- Immune System Evaluation: These tests provide insights into an individual’s immune system function and response to specific antigens.
- Pregnancy and Maternal Health: Titer tests are vital for pregnant women to ensure the safety of both the mother and the fetus.
8. Applications in Healthcare
Ana titer tests have diverse applications in healthcare settings:
- Infectious Disease Control: They assist in identifying and controlling the spread of infectious diseases by determining immunity levels.
- Transfusion Medicine: Titer tests are used to match blood donors and recipients, ensuring compatibility and reducing the risk of adverse reactions.
- Organ Transplantation: Evaluating titer values helps in selecting suitable organ donors and managing immunosuppressive therapy.
- Research and Development: Titer tests contribute to medical research, vaccine development, and understanding immune responses.
9. Factors Affecting Titer Results

Several factors can influence the accuracy and interpretation of ana titer results:
- Timing of Testing: The timing of the test relative to exposure or vaccination can impact the results.
- Individual Variability: Different individuals may have varying immune responses, leading to differences in titer values.
- Sample Handling: Proper sample collection, storage, and transportation are crucial to maintain the integrity of the results.
- Laboratory Techniques: The specific techniques and reagents used in the laboratory can affect the accuracy of the test.
10. Titer Testing and Vaccination
Ana titer tests are often used in conjunction with vaccination programs:
- Pre-Vaccination Testing: Titer tests can be performed before vaccination to assess an individual’s immunity and determine the need for vaccination.
- Post-Vaccination Testing: After vaccination, titer tests are used to confirm the development of immunity and ensure effective protection.
- Booster Shots: If titer values decline over time, booster shots may be recommended to maintain immunity.
11. Monitoring Immune Response
Ana titer tests are valuable tools for monitoring an individual’s immune response over time:
- Disease Progression: Titer values can indicate the progression or resolution of an infection, helping in disease management.
- Immune Disorders: In cases of immune system disorders, titer tests can assist in diagnosing and monitoring the condition.
- Treatment Efficacy: Titer values provide insights into the effectiveness of treatments, especially in immunotherapy.
12. Limitations and Challenges
While ana titer tests are valuable, they do have certain limitations:
- False Positives/Negatives: Like any laboratory test, there is a possibility of false positive or false negative results due to various factors.
- Interpretation Complexity: Interpreting titer results requires expertise, as different antigens may have varying titer values.
- Sample Quality: The quality of the blood sample and its handling can impact the accuracy of the test.
- Cross-Reactivity: In some cases, antibodies may cross-react with similar antigens, leading to misinterpretation.
13. Importance of Healthcare Professional Guidance
When interpreting ana titer results, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional:
- Expertise: Healthcare professionals have the knowledge and experience to accurately interpret titer values.
- Individualized Approach: They can consider the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and other factors to provide a personalized interpretation.
- Treatment Recommendations: Based on the titer results, healthcare professionals can recommend appropriate treatments or further investigations.
14. Titer Testing and Travel
Ana titer tests are often required for international travel, especially to certain regions with specific health risks:
- Yellow Fever: Many countries require a yellow fever titer test and vaccination certificate for entry.
- Meningococcal Disease: Titer tests and vaccinations may be recommended for travel to areas with a higher risk of meningococcal disease.
- Other Travel-Related Infections: Depending on the destination, titer tests and vaccinations may be advised for diseases like typhoid, hepatitis A, and cholera.
15. Future Developments in Titer Testing
The field of titer testing is continuously evolving, with ongoing research and advancements:
- Advanced Techniques: Newer, more sensitive laboratory techniques are being developed to improve the accuracy and speed of titer tests.
- Point-of-Care Testing: Efforts are being made to develop rapid, point-of-care titer tests for faster and more accessible results.
- Digital Health Integration: Integrating titer testing with digital health platforms can enhance data management and patient monitoring.
- Personalized Medicine: Titer testing may play a role in personalized medicine, allowing for tailored treatment and prevention strategies.
Conclusion
Ana titer tests are powerful tools in medical diagnostics, offering valuable insights into an individual’s immune response and health status. Understanding the results and their implications is crucial for healthcare professionals and patients alike. By interpreting titer values accurately and considering individual factors, medical professionals can make informed decisions regarding vaccination, disease management, and patient care. As the field of titer testing advances, we can expect even more accurate and accessible tools to enhance our understanding of immune responses and improve overall healthcare.
FAQ
What is the purpose of an ana titer test?

+
An ana titer test is used to measure the concentration of antibodies in the blood, providing information about an individual’s immune response to specific antigens.
How is a titer test different from other blood tests?
+
Titer tests specifically measure the quantity of antibodies, while other blood tests may analyze various components like blood cells, enzymes, or hormones.
Can ana titer tests detect all types of infections?

+
No, ana titer tests are designed to detect specific antibodies against known antigens. The choice of test depends on the suspected infection or vaccine.


